Imagine creating stunning, lifelike images with just a few words. That’s the power of AI image prompts, a breakthrough technology transforming how we approach visual creation.
Whether you’re designing captivating social media graphics, crafting intricate game characters, or even generating hyper-realistic product photography, AI image prompts allow you to breathe life into your ideas through simple text inputs.
AI platforms like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, Dall-E, Meta AI, and Gemini harness the full potential of machine learning and neural networks, making the impossible possible.
These advanced systems turn your written descriptions into vivid, detailed visuals, blending creativity with cutting-edge technology. With the support of models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models, the range of images you can generate is limitless, from lifelike photos to dreamy abstract art.
What’s more, AI image prompts are accessible to everyone. You don’t need to be a professional artist to produce high-quality visuals. By mastering the art of prompt crafting, you can use these tools to unlock a world of possibilities if you’re looking to lift your branding, create mind-blowing game environments, or simply experiment with art.
Throughout this article, we’ll dive deep into the magic of AI image prompts, exploring how they work, the types of prompts you can use, and how to make them work across different AI models. Ready to see what your words can create? Let’s get started.
What Are AI Image Prompts?
AI image prompts are written instructions that describe what kind of image a user wants an AI model to create. These prompts use natural language and can include details such as the subject, setting, style, lighting, or mood of the image.
When a prompt is submitted, the AI interprets the words and generates a visual result based on those descriptions. This process is called “text-to-image generation”.
The core idea behind an AI image prompt is simple: it acts like a blueprint for the image the user has in mind.
The AI uses machine learning models trained on large datasets of images and captions to understand how certain words relate to visual elements.
A well-structured prompt gives the AI more accurate guidance and leads to better image quality and alignment with the user’s vision.
For example, if someone types a prompt like:
“a futuristic city with neon lights at night, in cyberpunk style, ultra-detailed, 8K resolution,”
The AI will attempt to recreate a city scene with those exact elements: futuristic architecture, glowing lights, a nighttime setting, and a specific visual style. The words in the prompt serve as entities and attributes, guiding the model’s creative process.
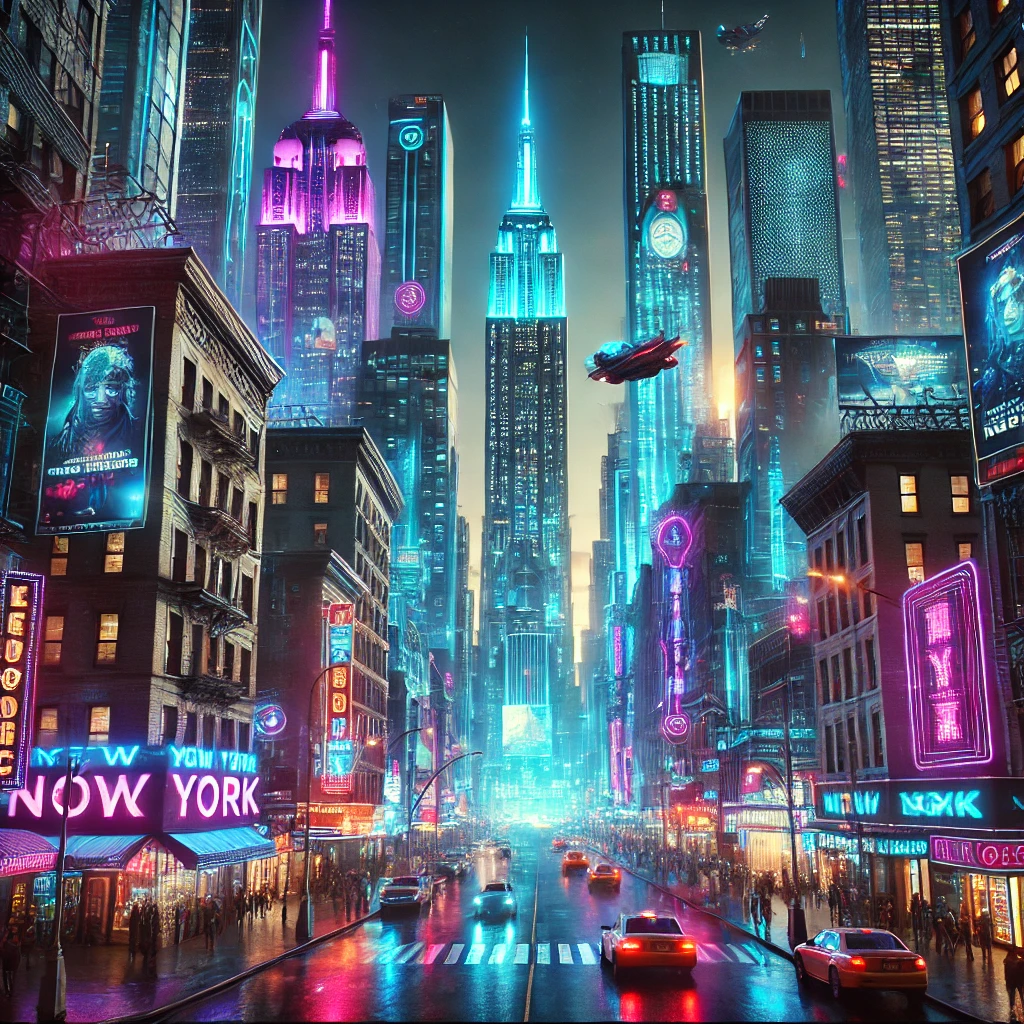

AI image prompts are widely used in digital art, product design, advertising, gaming, and social media content. They help creators generate visuals without needing photography or manual illustration.
The way prompts are written, the choice of words, the order, and the specificity play a major role in shaping the outcome.
Some of the most popular tools that convert text prompts into images include DALL-E by OpenAI, Stable Diffusion by Stability AI, MidJourney, Adobe Firefly, Google Imagen (Prototype), Bing Image Creator, Canva’s AI Image Generator, Make-A-Scene (Meta), and CM3Leon (Meta).
Each tool has its strengths in terms of style, detail, or realism, but all depend on prompt quality to deliver the best results. The ability to write clear and detailed prompts is now considered a key skill in working with generative AI tools.
What Is the Definition and Significance of AI Image Prompts?
AI image prompts are natural language inputs that instruct an artificial intelligence model to create a specific visual output. These prompts work as a bridge between human language and machine-generated visuals.
The AI system reads the text, understands the intent behind it, and produces an image that matches the description.
The definition of an AI image prompt lies in its function; it is a text-based command used in a generative AI environment to turn ideas into visual content.
These prompts can describe objects, scenes, lighting, perspective, art style, or emotions. They are used with text-to-image models like DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion, which are trained to interpret language and generate images from it.
The significance of AI image prompts comes from their role in creative automation. Designers, marketers, and artists use prompts to generate content quickly and at scale. Instead of manually creating a visual, they type what they want, and the AI provides instant image variations. This speeds up workflows, saves resources, and allows more room for experimentation.
For example, typing:
“a cozy wooden cabin in the forest during snowfall, hyper-realistic, warm lighting”
Into a model like Stable Diffusion results in an image that includes all of those attributes.
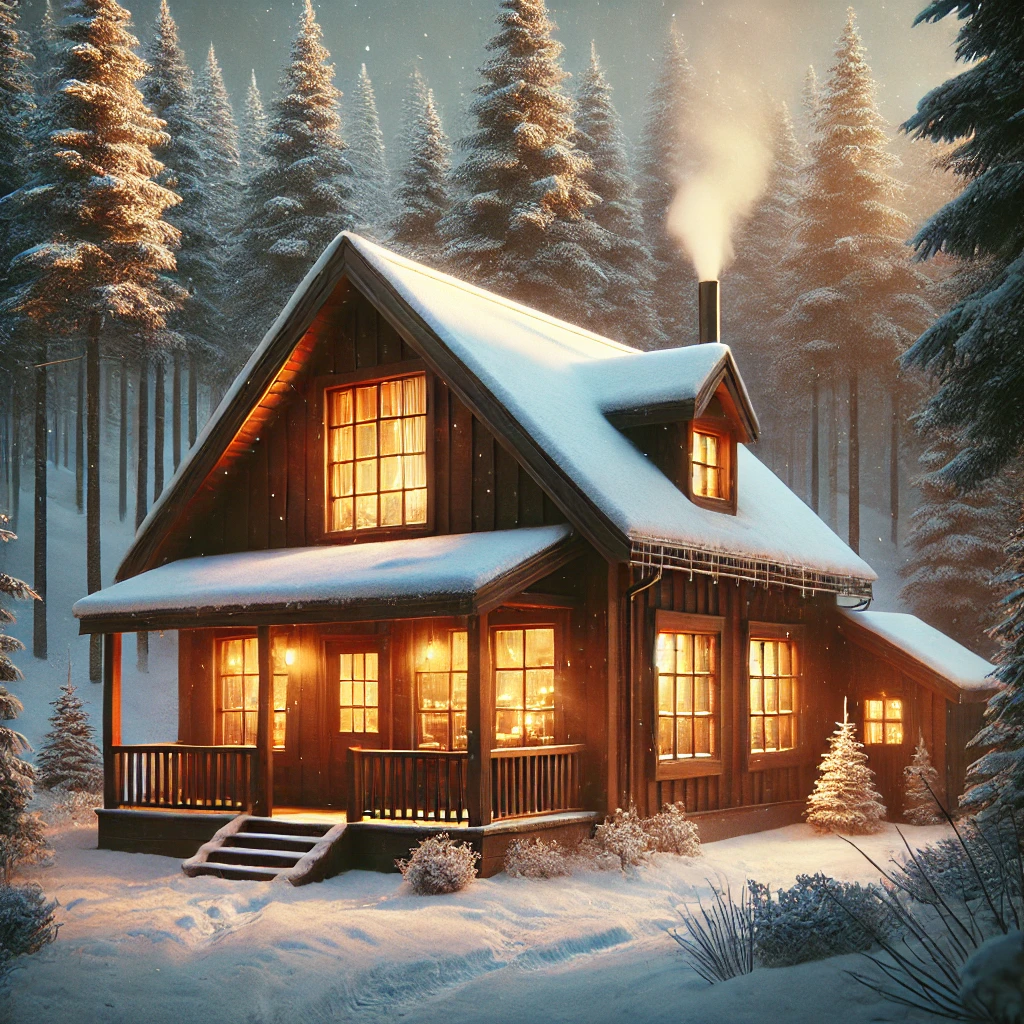

The AI recognizes entities such as “cabin,” “forest,” and “snowfall,” interprets modifiers like “hyper-realistic” and “warm lighting,” and generates a detailed output based on that structure.
AI image prompts are part of a larger field called prompt engineering, where the phrasing, order, and specificity of words matter. Well-crafted prompts lead to better images. Poorly structured ones can result in distorted or irrelevant visuals. Understanding how language maps to visual concepts is essential for getting the most out of text-to-image tools.
The rise of prompt-based image generation is changing how visual content is created. As AI tools evolve, the role of prompts becomes even more important, not just as instructions but as the core mechanism behind AI creativity.
How Do AI Models Interpret Text-to-Image Prompts?
AI models process image prompts by first breaking the input text into smaller language units. This process is called tokenization. Look at the flowchart given below, the whole process from prompt to image generation is shown step by step clearly.
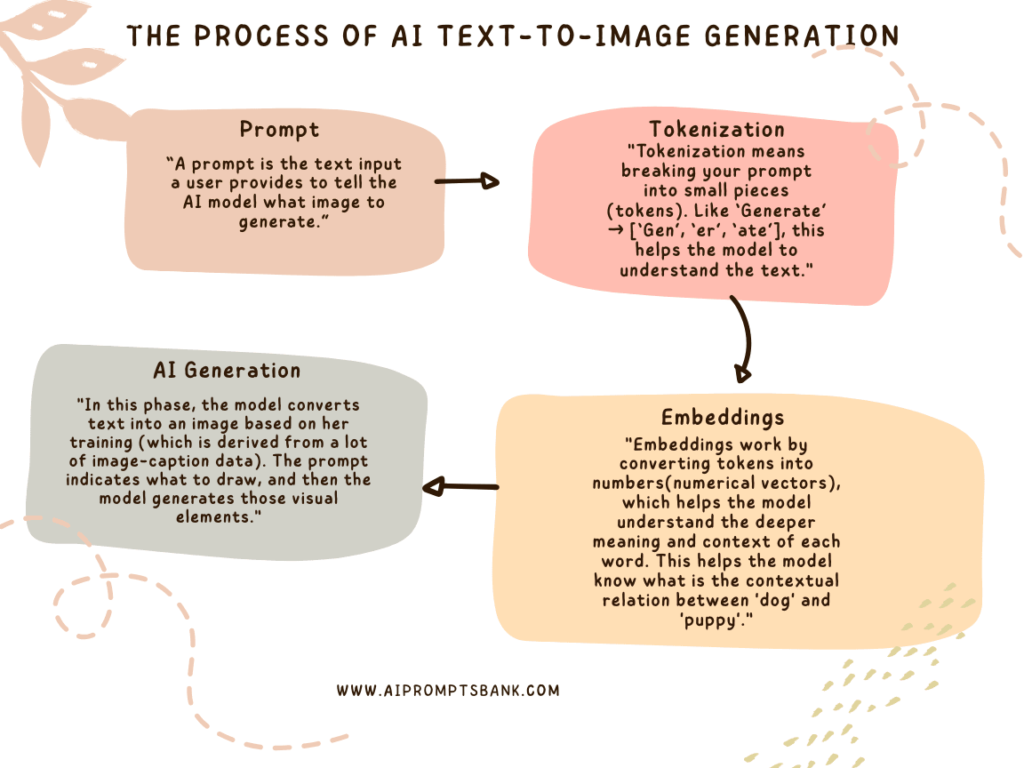
These tokens are then converted into numerical vectors using text embedding, which helps the model grasp the semantic meaning and context behind each word.
Once the language is encoded, the AI model maps the prompt to learned visual representations. This connection between language and imagery is built using large datasets of image-caption pairs. It allows the system to match objects, scenes, styles, and moods with specific words or phrases.
For instance, a prompt like:
“a red sports car on a winding mountain road, during golden hour, ultra-realistic”
provides multiple layers of information: the subject (“car”), the environment (“mountain road”), the lighting condition (“golden hour”), and the visual style (“ultra-realistic”). Each part of the sentence acts as an instruction.
Models such as DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion interpret these instructions using neural networks.
These networks use diffusion or transformer-based architectures to synthesize the final image from the text input. The diagram below shows this process, starting with text embedding, which converts the input text into numerical data. The neural network then processes this data using a diffusion or transformer model, ultimately generating the final image.
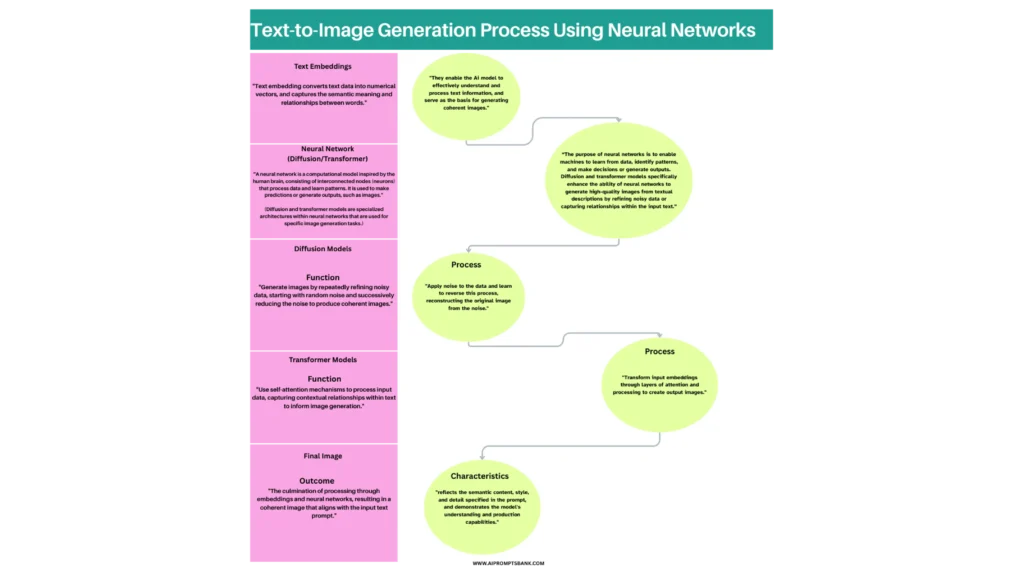
Prompt interpretation relies on lexical cues like object names, style descriptors, lighting terms, and emotional tones. Clear, descriptive prompts with structured phrasing lead to more accurate, detailed, and visually coherent outputs.
The 2025 AI Image‑Generation Toolbox (Diffusion, GAN, Transformer, NeRF)
This detailed paragraph provides a comprehensive overview of various image-generation tools, categorized by their underlying technology and application.
These range from text-to-image diffusion models (both hosted and open-source) and GAN-based generators to transformer models and multimodal chatbots with integrated image-creation capabilities.
The data also covers specialized tools for 3D generation, video creation, generative editing, upscaling, avatar building, on-device solutions, and neural style transfer.
| Category | Tool | Specialty / Notes | Free ? / Where |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffusion – SaaS | DALL-E 3 | High prompt‑fidelity, text rendering | Paid credits in ChatGPT Plus / Copilot Designer |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Midjourney v6–v7 | Stylised art, Discord workflow | Subscription (no free tier) |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Adobe Firefly Image 3 | Photoshop “Generative Fill” engine | Freemium Adobe credits |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Google Imagen 3 (ImageFX) | Photorealism + accurate text | Limited free quota (Google Labs) |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Gemini 2.0 Flash | Native image output in Gemini Advanced | Included in Google One AI Premium |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Ideogram 2.0 | Best‑in‑class typography | Freemium (10 credits / day) |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Leonardo.Ai | Multi‑model studio (Phoenix, Alchemy…) | Freemium → paid tiers |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Playground v2 | Fast SDXL‑based diffusion | Generous free tier |
| Diffusion – SaaS | NightCafe | Community gallery & challenges | Freemium credit loops |
| Diffusion – SaaS | BlueWillow | Discord‑based, social prompts | Freemium |
| Diffusion – SaaS | StarryAI | Mobile‑friendly app | Freemium |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Canva “Magic Media” | One‑click graphics in Canva editor | Free / Pro boosts |
| Diffusion – SaaS | Microsoft Designer | Marketing creatives via Copilot | Free with Microsoft account |
| Diffusion – Open Source | Stable Diffusion 1.5 → SDXL 1.0 | De‑facto standard checkpoints | Free weights, self‑host |
| Diffusion – Open Source | SDXL Turbo | Latency‑optimised SDXL | Free research weights |
| Diffusion – Open Source | Stable Cascade | Multi‑stage fast diffusion | Free |
| Diffusion – Open Source | SD 3 preview | Next‑gen Stable Diffusion | Free (research) |
| Diffusion – Open Source | Kandinsky 3 | Multilingual open weights | Free (Apache‑2.0) |
| Diffusion – Open Source | DeepFloyd IF | High‑fidelity, crisp text | Free R&D licence |
| Diffusion – Open Source | PixArt‑σ / α | 4 K transformer‑diffusion hybrid | Free |
| Diffusion – Open Source | Stable Lightning / LinFusion | Distilled, super‑fast SDXL | Free |
| Diffusion – Open Source | ComfyUI | Node‑graph GUI, ControlNet | Free desktop |
| Diffusion – Open Source | AUTOMATIC1111 | Feature‑rich web UI | Free |
| Diffusion – Open Source | DiffusionBee | Offline macOS app | Free |
| GAN | GigaGAN | 16‑MP images in <4 s | Open‑source (MIT) |
| GAN | StyleGAN 3 | Style mixing, face avatars | Free weights |
| GAN | Artbreeder | Web mash‑ups, genetics sliders | Freemium |
| GAN | GauGAN 2 / NVIDIA Canvas | Paint‑to‑image landscapes | Free desktop (RTX GPUs) |
| GAN | DragGAN / FreeDrag | Post‑generation warp editing | Open‑source demos |
| Transformer / AR | Parti | Autoregressive pioneer | Research code |
| Transformer / AR | ImageGPT | Autoregressive pioneer | Research code |
| Transformer / AR | DiT family | Transformer‑diffusion hybrids | Open weights |
| Transformer / AR | PixArt‑σ | 4 K transformer‑diffusion | Free |
| Transformer / AR | CogView 3 | Chinese prompt specialist | Free API (Baidu) |
| Transformer / AR | ERNIE‑ViLG 2.0 | Chinese prompt specialist | Free API (Baidu) |
| Multimodal Chatbot | Gemini Advanced | Gemini Flash diffusion | Google One AI Premium |
| Multimodal Chatbot | Grok (xAI) | Grok Aurora image head | X Premium + |
| Multimodal Chatbot | ChatGPT Plus | GPT‑4o + DALL·E 3 | $20 / mo |
| Multimodal Chatbot | Copilot (Bing) | DALL·E 3 via GPT‑4‑Turbo | Free Microsoft account |
| 3‑D / NeRF | DreamFusion / Magic3D / DreamGaussian | Text‑to‑mesh | Research code |
| 3‑D / NeRF | Luma AI | Mobile NeRF capture, Dream Machine | Freemium iOS / web |
| 3‑D / NeRF | Blockade Labs Skybox | Instant 360° HDRIs | Freemium |
| 3‑D / NeRF | Kaedim | Game‑ready mesh cleanup | Paid SaaS |
| 3‑D / NeRF | Meshy.ai | Game‑ready mesh cleanup | Paid SaaS |
| Video Diffusion | OpenAI Sora | 1‑min HD video | Private beta |
| Video Diffusion | Runway Gen‑2 / 3 / 4 | Text‑to‑video + edit | Freemium credits |
| Video Diffusion | Pika 1.0 | Social‑length clips | Freemium |
| Video Diffusion | Luma “Dream Machine” | Video + 3‑D export | Wait‑list beta |
| Video Diffusion | Google Veo 2 | Long‑form video diffusion | Preview (Cloud Next 2025) |
| Generative Editing | Photoshop “Generative Fill & Expand” | In/out‑painting inside PS | Freemium Adobe credits |
| Generative Editing | ClipDrop | Remove, Uncrop, Relight | Freemium |
| Generative Editing | MGIE | Apple‑led text‑guided edits | Open‑source (MIT) |
| Upscale / Restore | Topaz Gigapixel AI v8 | 2×–6×, face detail | Paid desktop |
| Upscale / Restore | Let’s Enhance / Claid.ai | Bulk e‑commerce upscales | Freemium SaaS |
| Upscale / Restore | Real‑ESRGAN | Open‑source SR | Free |
| Upscale / Restore | GFPGAN | Face restoration | Free |
| Upscale / Restore | ClipDrop Upscaler | SDXL‑based SR | Freemium |
| Avatar / Character | Lensa “Magic Avatars” | 10–20 selfie fine‑tune | Paid per pack |
| Avatar / Character | Fotor AI Portrait | Stylised profile pics | Freemium |
| Avatar / Character | ArtSmart AI | Stylised profile pics | Freemium |
| Avatar / Character | StyleGAN‑Human | Full‑body avatars | Free weights / paid SaaS |
| Avatar / Character | AvatarAI | Full‑body avatars | Paid SaaS |
| Avatar / Character | HeyGen | Talking‑head video | Paid credits |
| Avatar / Character | Reface / Revive | Face‑swap GIF/video | Freemium mobile |
| On‑Device | DiffusionBee | SDXL offline on macOS | Free |
| On‑Device | InvokeAI | Easy local pipeline | Free |
| On‑Device | Fooocus | One‑click local GUI | Free |
| On‑Device | Krita “Dream‑Art” plug‑in | Painter workflow | Free (GPL) |
| On‑Device | Paint.NET AI Assistant | Lightweight Windows editor | Freemium |
| Neural Style Transfer | Prisma | 700+ mobile filters | Freemium |
| Neural Style Transfer | DeepArt.io | Classic NST web app | Paid renders |
| Neural Style Transfer | Adobe “Neural Filters” | Portrait relight, style | Photoshop subscription |
What Are the Core AI Concepts Behind Image Prompts?
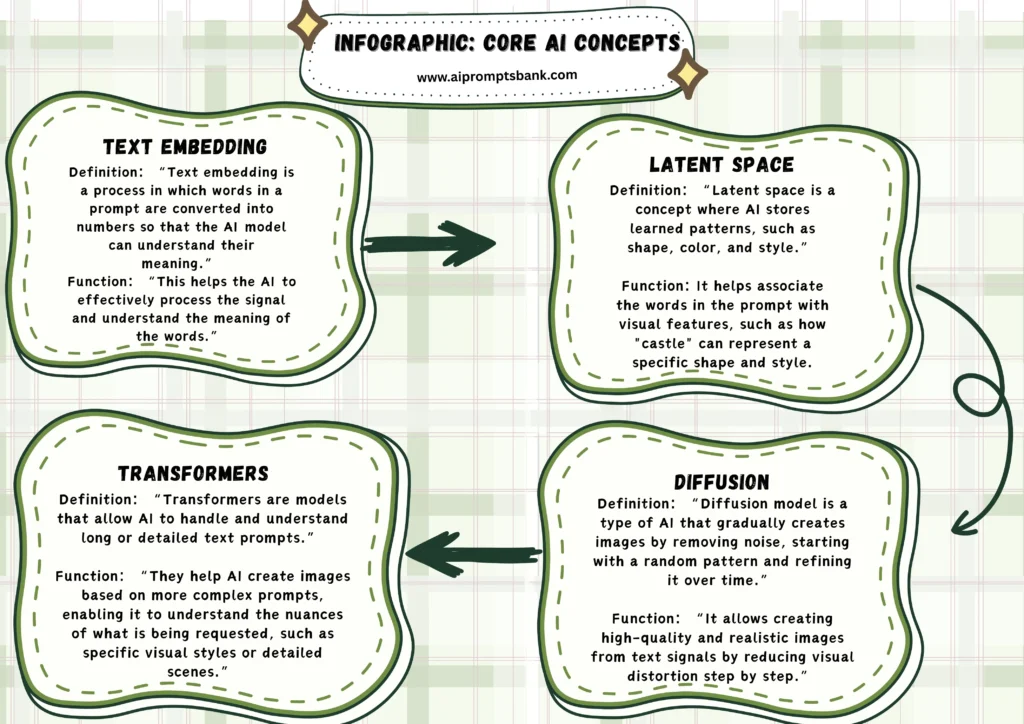
AI image prompts work because of models that connect language with visuals. These models use deep learning to understand what the prompt says and turn it into an image.
One key concept is text embedding. It helps the model understand the meaning of words in a prompt. The words are turned into numbers so the AI can process them.
Another concept is latent space. This is where the model stores patterns it has learned, like shapes, colors, and styles. It uses this space to match words with image features.
AI tools like DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion use either diffusion models or GANs. Diffusion models slowly build images by removing noise. GANs use two networks to generate and check images.
Most models use transformers, which help the AI understand long or detailed prompts. For example, in the prompt “A castle on a snowy hill at night, in oil painting style,” the AI understands what to draw, how it should look, and what style to use.
These core ideas, embedding, latent space, diffusion, and transformers, help AI turn simple text into complex images.
How Do GANs Influence AI-Generated Images?
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a type of AI model used to create realistic images. A GAN has two parts: a generator that makes images and a discriminator that checks if they look real. These two networks compete with each other. As the generator improves, the images get more detailed and lifelike.
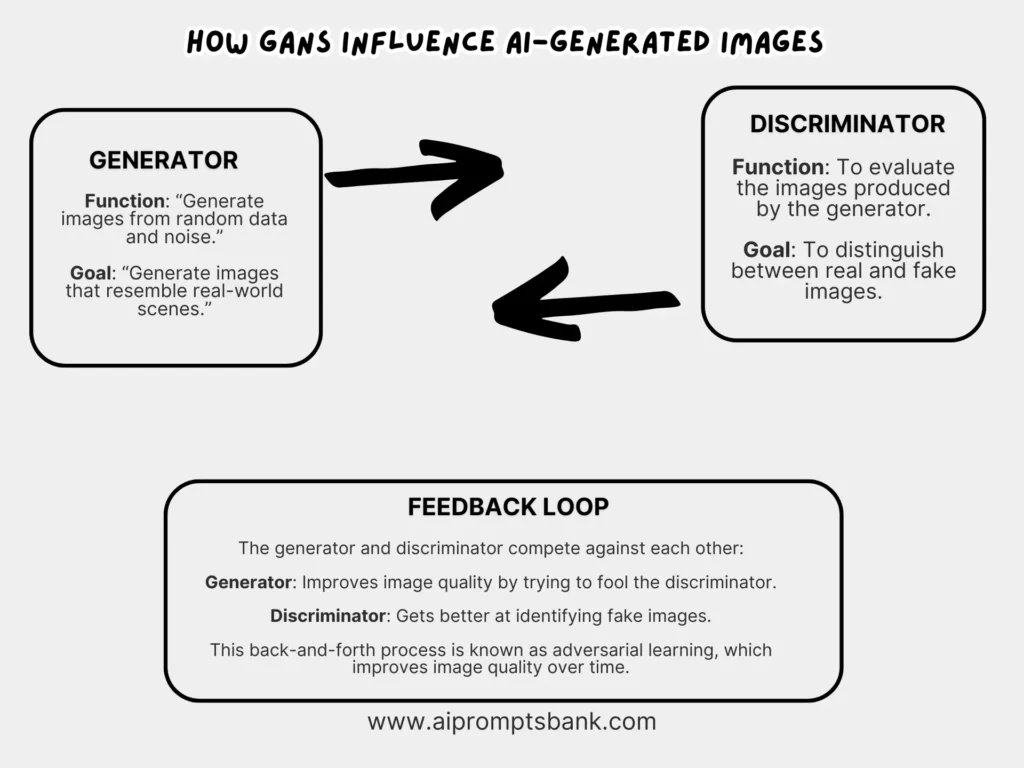
GANs learn by training on large sets of real images. The generator tries to fool the discriminator, while the discriminator gets better at spotting fake images. This back-and-forth process is called adversarial learning. It helps the model improve image quality over time.
GANs are known for creating sharp and high-resolution images, especially in areas like face generation, art synthesis, and photo-realistic textures. They can also mimic specific styles if trained on examples, making them useful for creative and branding purposes.
For example, a GAN trained in portrait photography can create a new human face that doesn’t exist but looks completely real. This is how tools like StyleGAN work.
Although newer models like diffusion models are now more popular for text-to-image generation, GANs played a major role in early AI art systems and still power many applications where visual realism matters most.
What Are the Differences Between GANs and Diffusion Models?
GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) and diffusion models are two types of AI architectures used to generate images, but they work in very different ways.
GANs use a two-part system: a generator that creates images and a discriminator that judges if they are real or fake. These models improve through competition. This method can produce sharp and high-quality images, but GANs can be unstable and may struggle with complex prompts or fine details.
Diffusion models, like those used in Stable Diffusion or DALL-E 2, take a slower, step-by-step approach. They start with random noise and gradually remove it to form an image. This process is called denoising, and it gives diffusion models better control, detail, and stability.
The table below describes how diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion and DALL-E 2 use a slow, step-by-step approach to noise reduction, providing better control, detail, and stability than GANs.
| Feature | GAN Output | Diffusion Output |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Generates images quickly, in one go | Slower, generates images step-by-step |
| Image Quality | Sharp images but may lack finer details | High-quality, detailed, with more control |
| Prompt Handling | May struggle with complex prompts | Handles detailed, creative prompts better |
| Realism vs. Creativity | More realistic, less creative | More creative, artistic, with style control |
| Strength | Good for quick, high-quality results | Great for detailed and creative images |
| Example Models | StyleGAN, BigGAN | Stable Diffusion, DALL-E 2, MidJourney |
| Best Use Case | Portraits, objects, and quick generation | Art, complex scenes, and creative designs |
| Control over Style | Limited control over style | Excellent control over artistic style and mood |
A key difference is that GANs learn to create images all at once, while diffusion models generate images gradually. As a result, diffusion models are more reliable for text-to-image tasks and support features like prompt weighting, style control, and better prompt alignment.
For example, if you use the prompt:
“A forest at sunrise, hyper-realistic, wide-angle view,”
GAN may generate a sharp image quickly, but might miss lighting or perspective details. A diffusion model will take longer but is more likely to match the scene exactly as described.
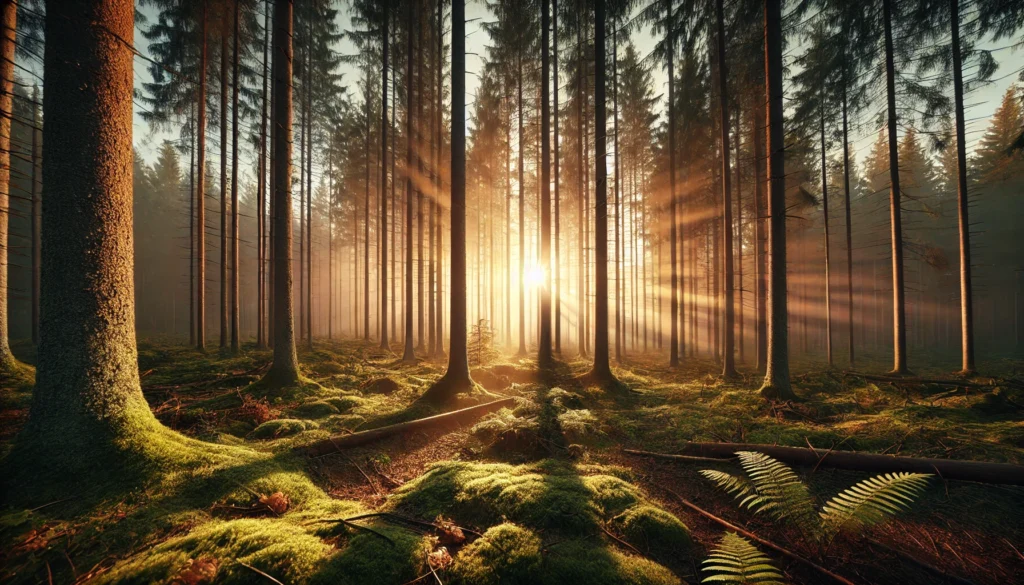

In summary, GANs are faster and known for sharp visuals, while diffusion models are slower but offer higher precision, better prompt handling, and more consistent results.
Why Are Diffusion Models Preferred Over GANs?
Diffusion models create images with better accuracy than GANs. They follow user prompts more closely and add more detail during image generation. Their step-by-step process gives users more control over how the image is formed.
GANs generate images all at once. They can produce sharp visuals, but they often miss parts of the prompt. They may also repeat patterns or create unrelated elements if the prompt is complex.
Diffusion models improve image structure, lighting, and style handling. They respond better to descriptive inputs and keep important details. This makes them more suitable for tasks like digital art, product mockups, and character design.
For example, the prompt:
“a mountain cabin in winter, soft lighting, oil painting style”
It will be more accurately followed by a diffusion model. The output will include all elements of the prompt in the correct order and style.

Modern tools like DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion, and Adobe Firefly use diffusion models. They are preferred for their precision, prompt alignment, and consistent image quality.
What Are Latent Diffusion Models and How Do They Work?
Latent diffusion models are used to create high-quality images from text. They work by first converting the image into a simpler form called a “latent space.” This space removes extra details while keeping important features.
Instead of working with full images, the model processes this smaller version. This makes training faster and generation more efficient. Once the image is ready, the model turns it back into a full image with all the details restored.
These models use a step-by-step method. They start with random noise and slowly adjust it to match the input prompt. This process helps the model follow the text more accurately and create better results.

For example, the prompt:
“a city skyline at sunset, watercolor style, soft colors”
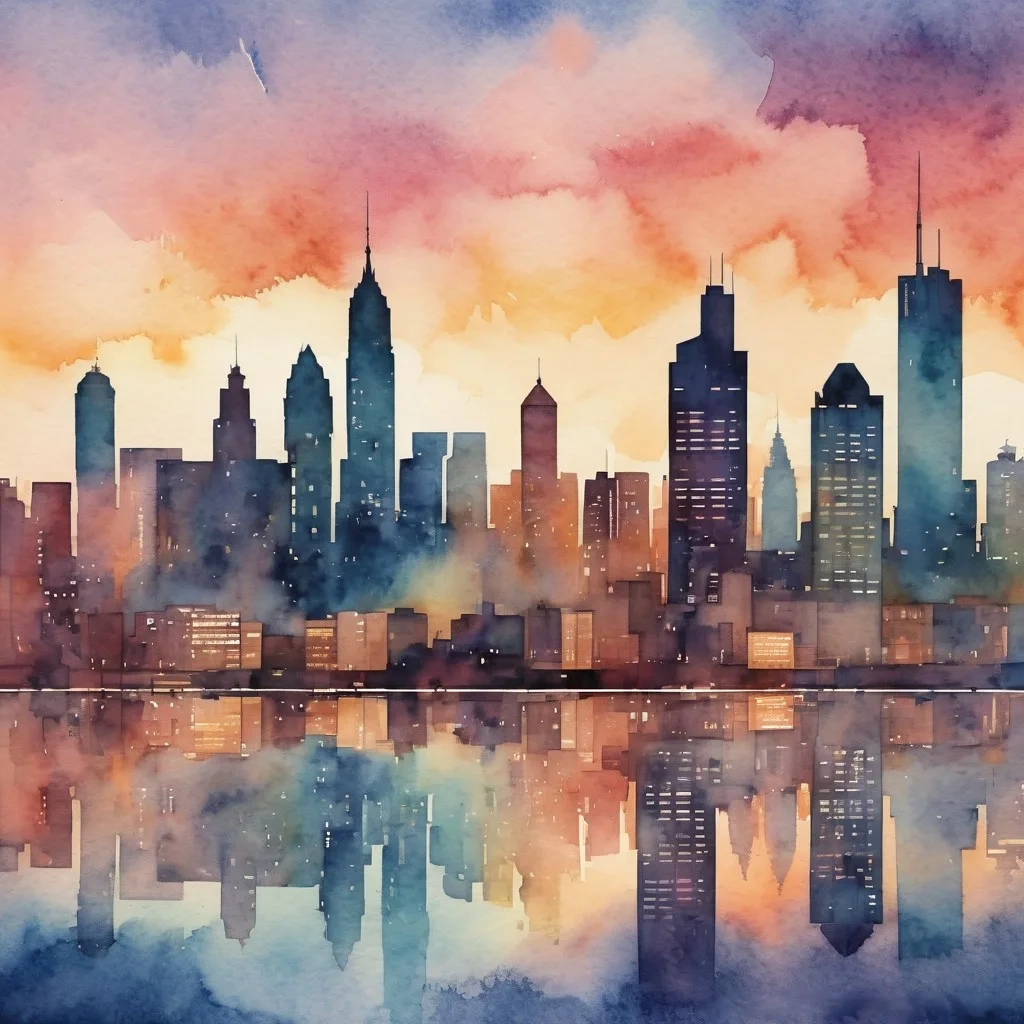

It goes through the latent space. The model uses the simplified version to shape the scene, and then converts it back into a detailed image.
Tools like Stable Diffusion use latent diffusion to balance speed, quality, and control. This method is preferred in many AI image tools because it keeps images clear while using less computing power.
How Does NLP Support Image Prompting?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps AI understand the meaning of prompts. It breaks the sentence into parts, checks grammar, finds important words, and understands the full context.
NLP turns the text into a form that AI models can use. This includes identifying the subject, action, style, and any extra details in the prompt. The clearer the structure, the better the model understands what to generate.
NLP tools use techniques like part-of-speech tagging, named entity recognition, and sentence parsing. These help the system focus on key information and ignore irrelevant words.
For example, in the prompt:
“a small child holding a red balloon in a foggy park,”
NLP helps the model know that “child” is the subject, “holding” is the action, and “foggy park” is the background.
Without NLP, models may miss details or misunderstand the prompt. NLP ensures the model can read natural language and turn it into correct image instructions.
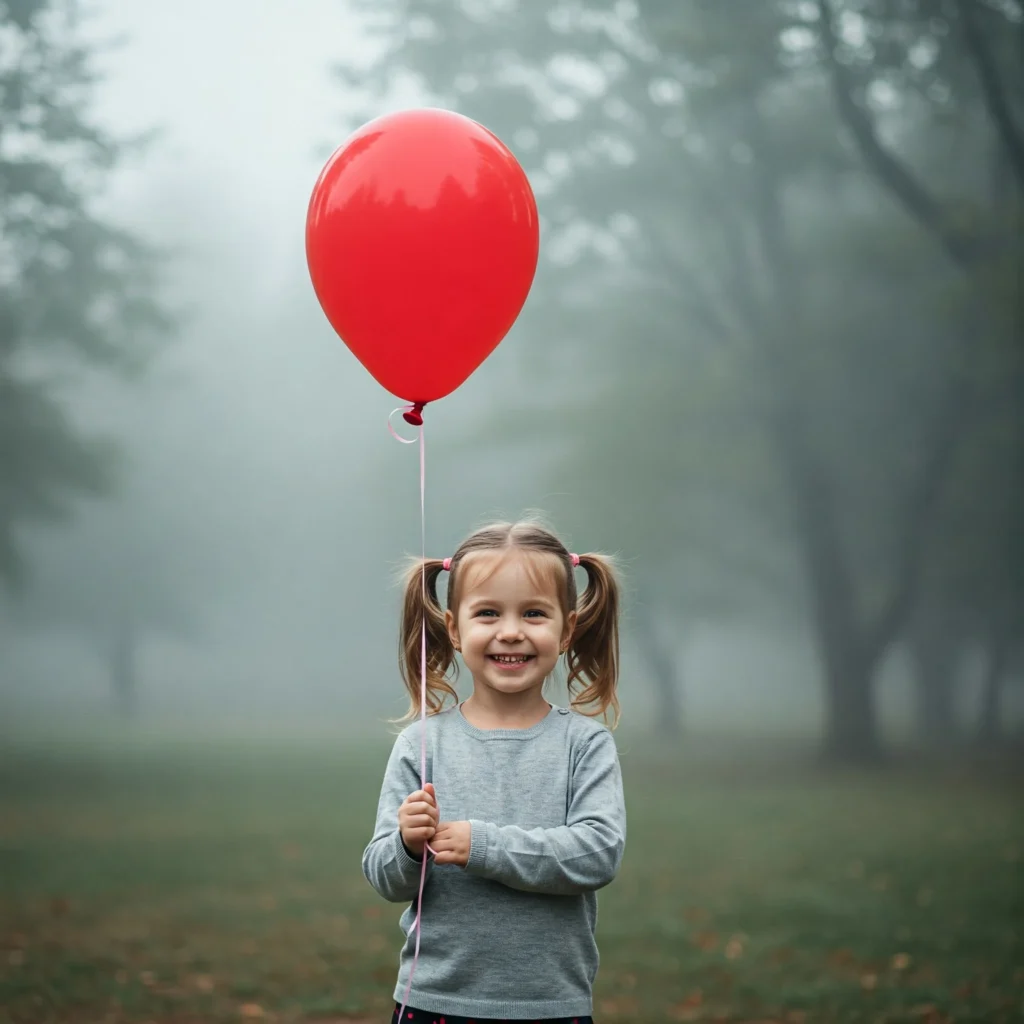

Text-to-image tools like DALL-E, Stable Diffusion, and MidJourney use NLP in the early processing stage to improve image accuracy.
How Does Text Embedding Improve Prompt Interpretation?
Text embedding helps AI models understand prompts more accurately. It changes each word or phrase in the prompt into a numeric form called a vector. These vectors keep the meaning and position of words.
The model uses these vectors to compare words, find patterns, and link them to visual features. This makes it easier for the model to understand what the user wants in the image.
For example, in the prompt:
“a peaceful lake surrounded by pine trees at sunrise,”
Text embedding helps the model link “peaceful” to mood, “pine trees” to scene elements, and “sunrise” to lighting.
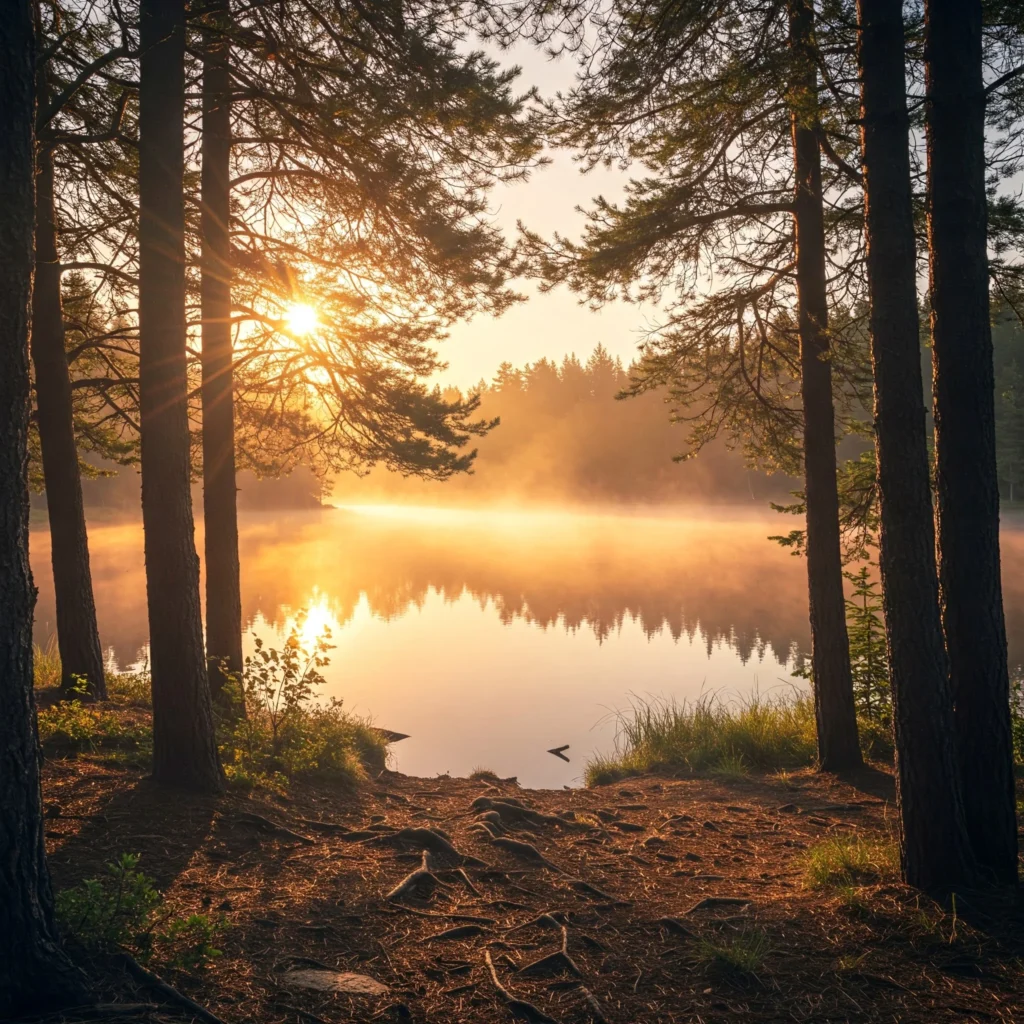

This process improves how the model reads and follows the prompt. It avoids confusion between similar words and keeps related words close together in the vector space.
Text embedding is used by tools like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and MidJourney to improve how well the image matches the text input.
What Are the Different Types of AI Image Prompts?
AI image prompts vary by use case and visual goal. Each type of prompt is written to match a specific purpose, style, or subject. The structure and keywords in the prompt change based on what kind of image the user wants to generate.
One common type is marketing and branding prompts. These prompts are used to create ads, product visuals, banners, or social media graphics. They focus on colors, emotions, and layout. For example, “a modern product display on a white background, clean and minimal style” is a typical prompt for e-commerce.
Gaming and 3D design prompts are used to create characters, weapons, or environments. These prompts often include camera angles, texture detail, or lighting setups.
Other types are illustration and concept art prompts. Artists use these to create digital paintings, storyboards, or environment sketches. The prompts include visual themes, art styles, and mood terms.
Photography prompts focus on realism. They help generate images that look like product shots, lifestyle photos, or portraits. The prompt includes details like lens type, lighting, and focus.
UI/UX prompts are used in app and web design. They help generate icons, splash screens, or layout elements. These prompts are short and style-driven.
Each type has a unique structure. Choosing the right prompt type improves image quality and relevance. AI tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E support all these use cases.
Marketing & Branding Prompts: Ad Creatives and Social Media Graphics
Marketing and branding prompts are written to generate visuals for ads, banners, social posts, and digital campaigns. These prompts focus on product visibility, color harmony, layout balance, and message clarity.
The main goal is to match the visual to a brand’s style. Prompts often include mood, color tone, lighting, and background keywords. A good marketing prompt helps create content that looks professional and grabs attention quickly.
For example, the prompt:
“a minimalist skincare product on a soft beige background, soft shadows, clean layout, high contrast”
It will create an image fit for an Instagram ad or product landing page. It tells the AI what the product is, how it should be styled, and what mood to deliver.
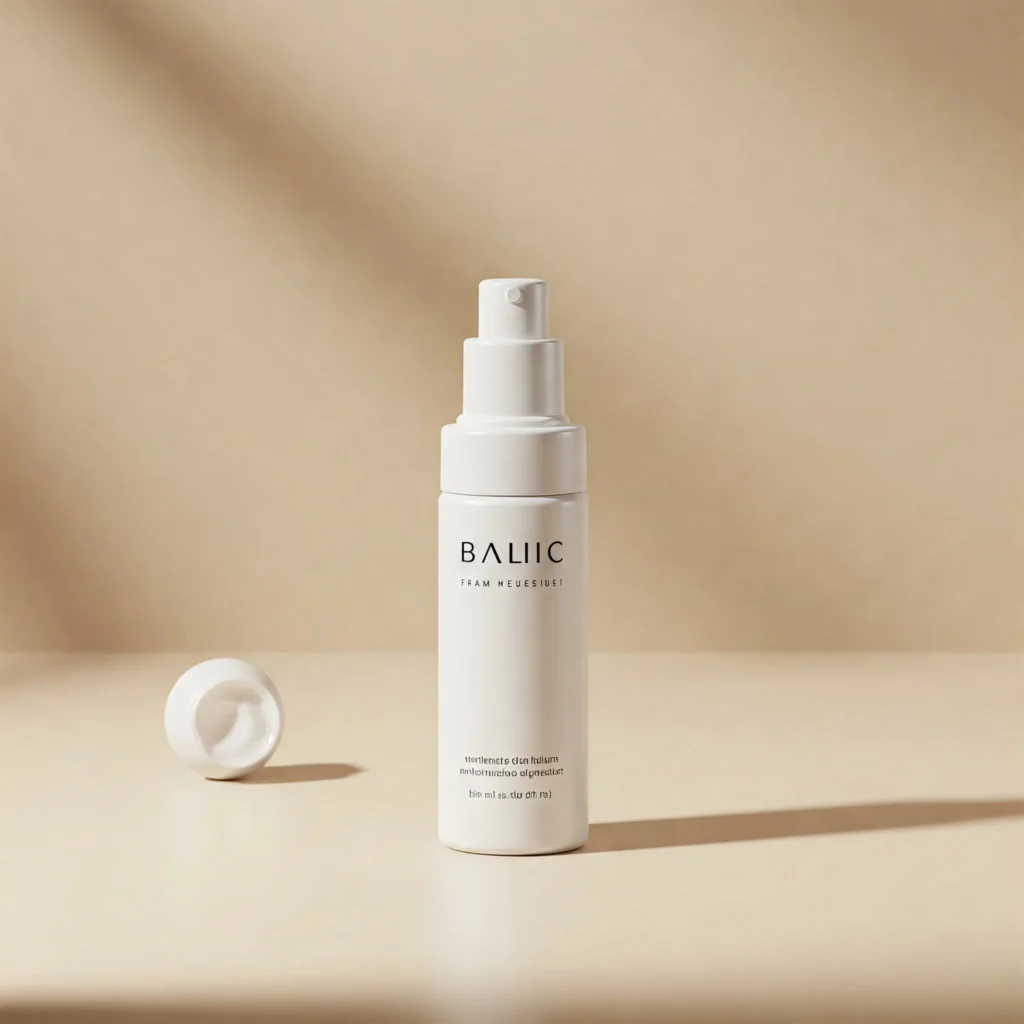

Branding prompts often include phrases like “flat lay,” “clean white space,” or “bold typography,” depending on the campaign. These prompts help maintain visual identity across all platforms.
AI tools like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and Adobe Firefly are used to produce ad-ready visuals quickly. This reduces production time and allows brands to test multiple creative styles before launch.
Effective AI Prompt Structures for Marketing Campaigns
AI prompt structures for marketing campaigns are written to clearly define the product, setting, style, and target emotion. A well-structured prompt helps the AI focus on what matters most for the brand message.
The structure should begin with the main subject (product or service), followed by scene setup, styling, and tone. The use of marketing-specific keywords like “premium,” “bold,” “natural,” or “luxury feel” helps guide the AI.
Good prompts avoid vague terms and use direct visual descriptors. This improves output quality and keeps the image consistent with the brand identity.
For example:
“a premium smartwatch on a dark background, top-down view, spotlight lighting, luxury tech style, sharp contrast, centered layout”
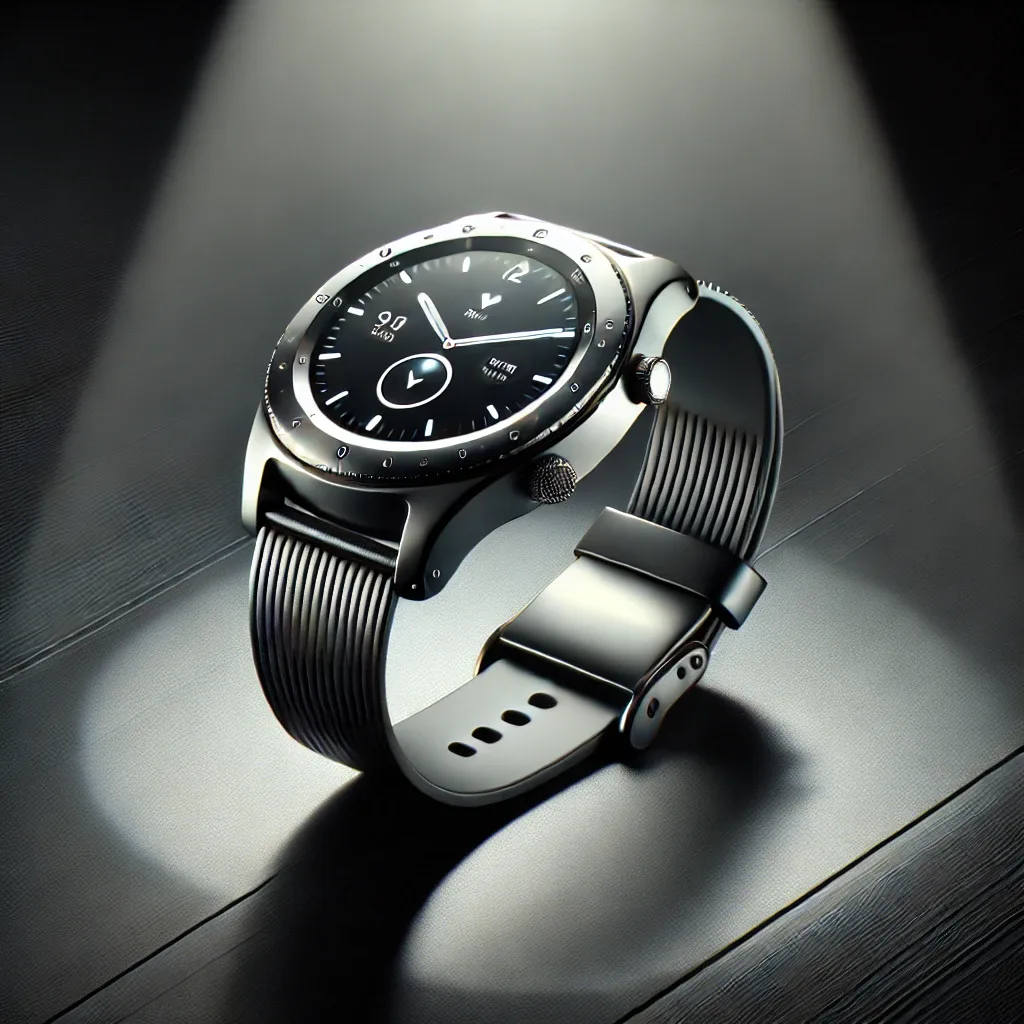

This prompt tells the AI exactly what to show, how to position it, and what mood to deliver. It suits high-end tech ads where focus and clarity are key.
Effective prompts often include attributes like camera angle (“top view”), color mood (“warm tones”), background type (“studio setting”), and design intent (“minimalist layout”).
Tools like DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion respond better when the prompt structure is clear, direct, and matches the visual goal of the campaign.
Enhancing Branding and Advertising Visuals Using AI-Generated Images
AI-generated images improve branding and advertising by giving teams fast, high-quality visuals tailored to campaign goals. These images match the brand tone, follow layout rules, and support consistent style across channels.
Marketers can generate visuals for banners, product displays, and hero images without needing photo shoots or manual editing. By adjusting the prompt, they can match the brand’s mood, message, and audience focus.
For example, a prompt like “a sleek running shoe on a reflective surface, high-contrast lighting, bold color background, athletic branding style” helps create a strong ad image that fits both website banners and social media posts.
Using AI, teams can test multiple visual directions, create seasonal themes, or adapt content for different platforms. This improves campaign flexibility and reduces production time.
Tools like Adobe Firefly, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion allow brands to enhance their visual assets while keeping control over tone, structure, and style.
Gaming & 3D Design Prompts: Character Design and 3D Game Elements
AI-generated prompts support game development by helping designers create 3D characters, props, and environments. These prompts are written with details like pose, armor, lighting, and texture style to match the game’s visual direction.
3D design prompts often include angles, materials, and mood. This helps the AI understand how to shape the object or character. Common keywords include “isometric view,” “realistic armor,” “fantasy style,” or “low-poly model.”
For example, the prompt:
“a sci-fi soldier in battle armor, standing pose, front angle, metallic texture, cinematic lighting, dark background”
AI can generate a full character concept that is ready for modeling or concept art.
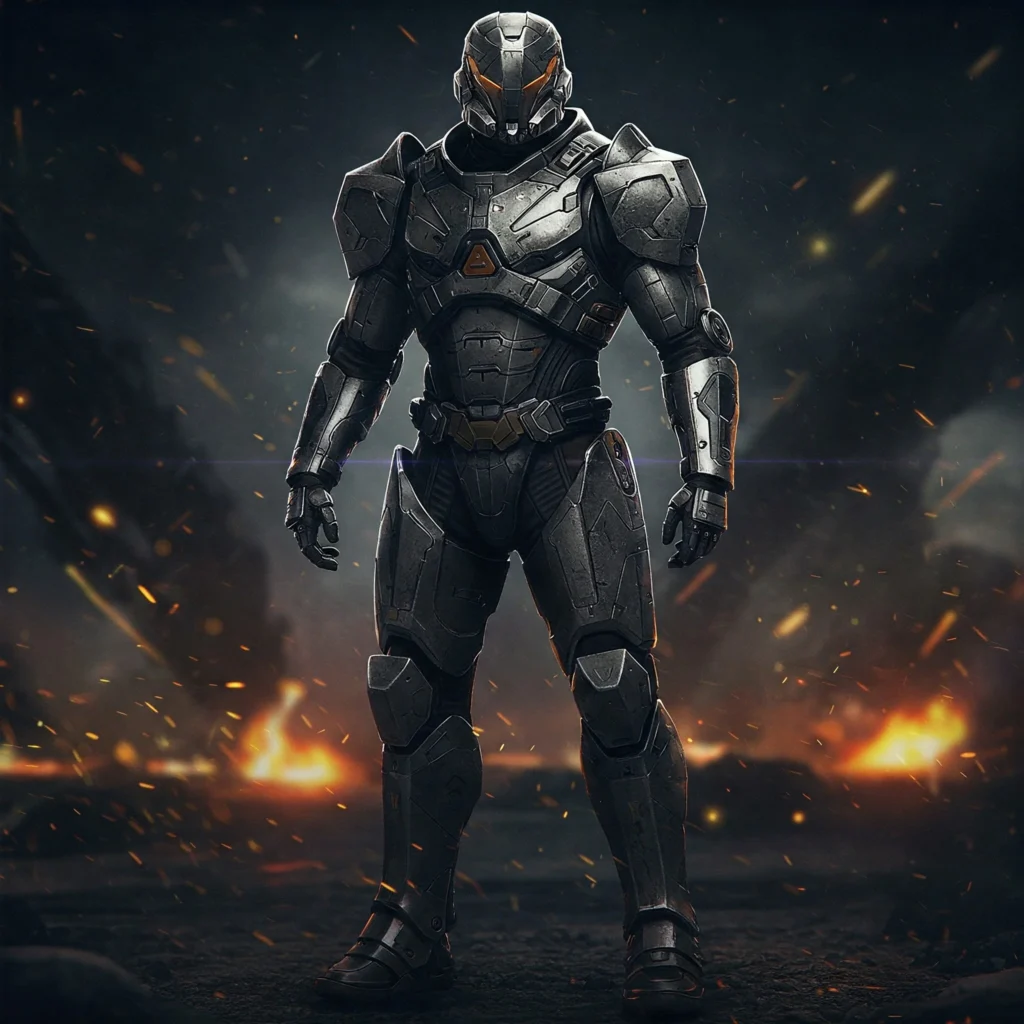

These prompts save time during early design stages. They give teams a clear visual base before moving into 3D software like Blender or Unity. Designers use them to explore options or present mockups quickly.
Tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and Leonardo AI are used for character design and 3D asset ideation. They help game teams test style, mood, and detail without manual sketching.
Illustration & Concept Art: Digital Paintings, Character, and Environment Design
AI image prompts help artists generate digital paintings and concept art quickly. These prompts are used to create characters, scenes, and fantasy worlds for games, films, or comics. They often include style, mood, pose, setting, and color tone.
Artists use terms like “brush texture,” “loose sketch,” “epic landscape,” or “dramatic lighting” to guide the AI. The goal is to build strong visual ideas that can later be refined or reworked by hand.
For example, a prompt like:
“a forest guardian in glowing armor, standing under moonlight, fantasy style, painterly texture, deep shadows”
It helps generate a base illustration for character concept development.
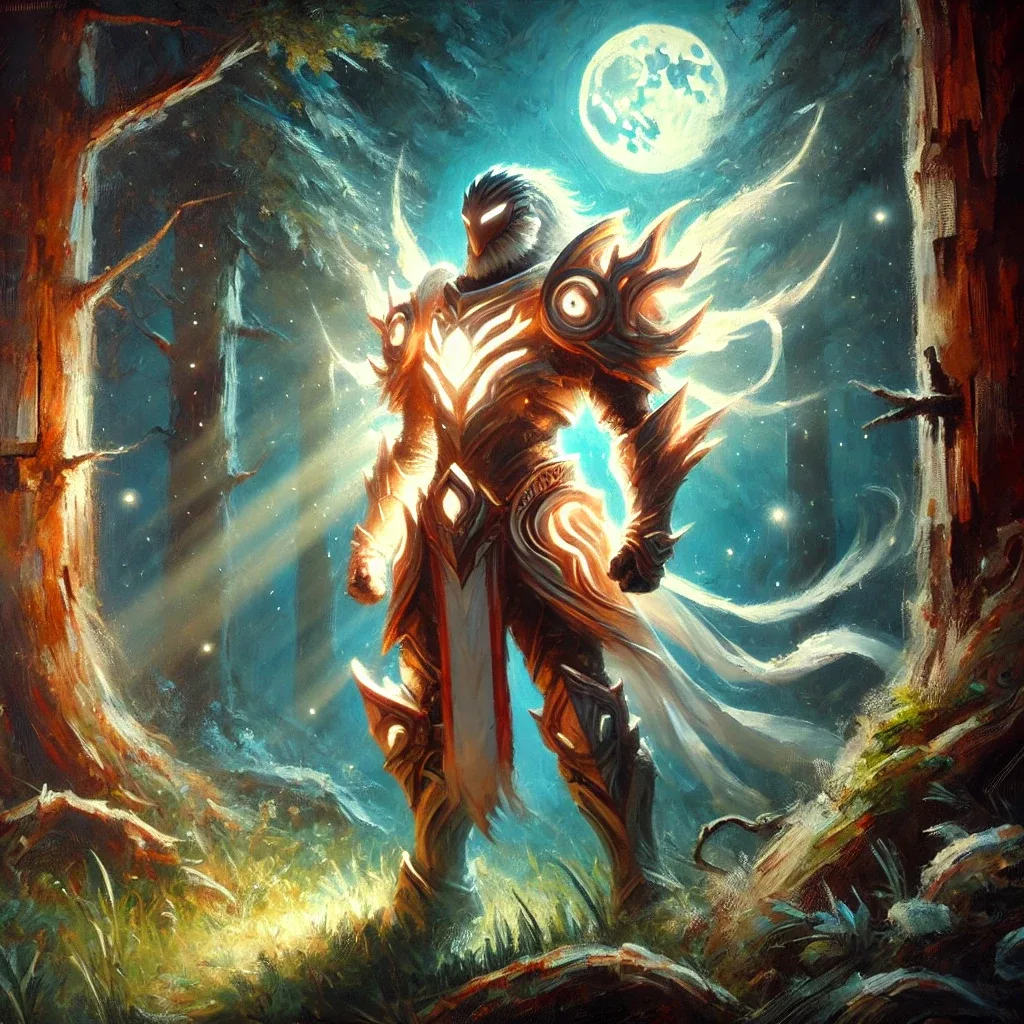

Environment prompts may describe the time of day, location, or atmosphere. Character prompts often focus on costume, emotion, and background elements.
Tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and Leonardo AI are used to generate high-quality art references. These outputs speed up brainstorming, storyboarding, and world-building in creative workflows.
Photography Applications: Product, Lifestyle, Event, and Portrait Photography
AI-generated photography prompts help create images for products, people, and real-world scenes. These prompts focus on camera angles, lighting setups, background, and emotion. They are useful for online stores, social campaigns, event posters, and profile photos.
Product prompts describe object type, surface, light reflection, and layout. Lifestyle prompts focus on actions, expressions, and location. Event photography prompts include crowd, stage, mood, or lighting. Portrait prompts add depth, eye contact, and color tone.
For example:
“a woman smiling in natural light, standing near a window, soft background blur, warm tones, portrait photography style”
This prompt gives a clear image structure for use in a bio, ad, or magazine feature.
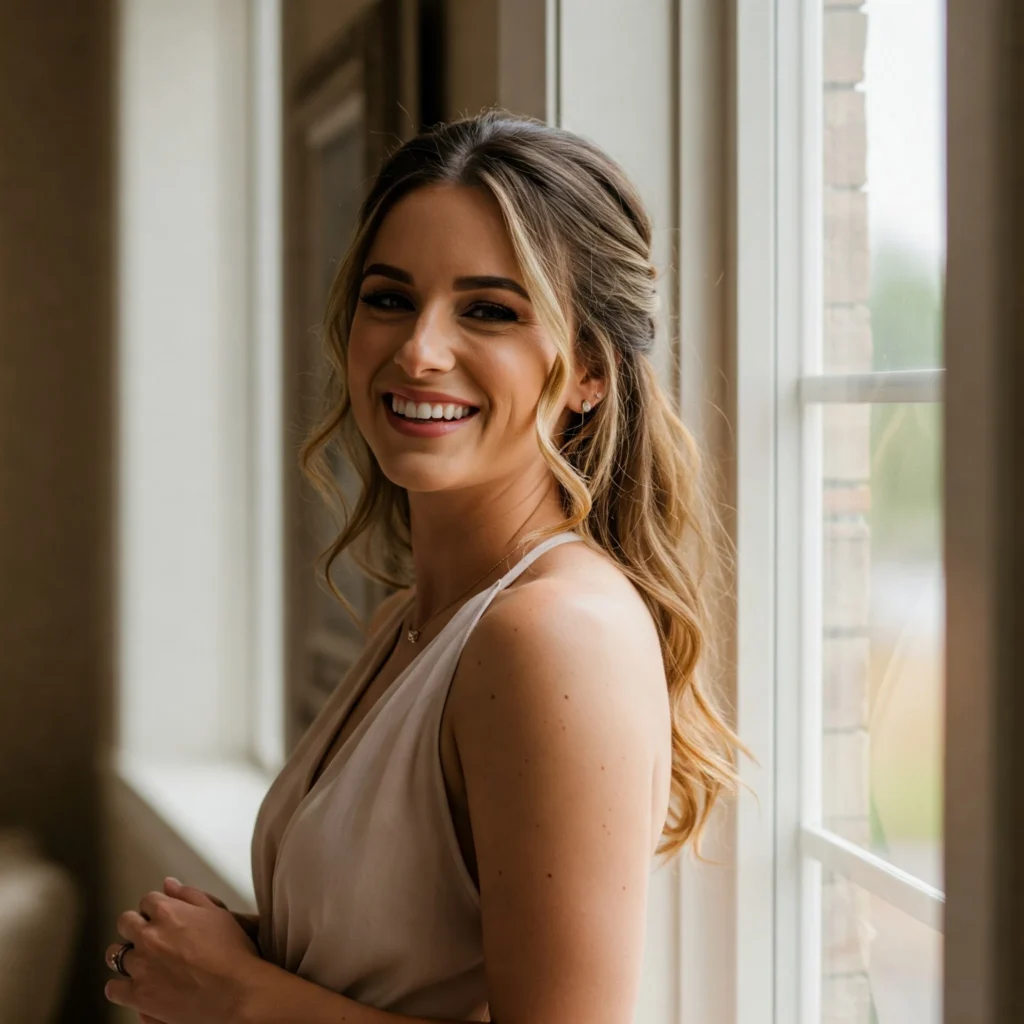

Tools like DALL-E, Adobe Firefly, and Stable Diffusion help generate images with correct framing, depth, and texture. These tools reduce the need for expensive photo shoots and speed up content production.
Generating Product Photography-Style Images for eCommerce Using AI Prompts
AI prompts help eCommerce teams create product images without cameras or physical setups. These images follow standard product photography rules such as clear lighting, centered focus, neutral background, and high resolution.
A good prompt includes the product type, surface texture, angle, and background. This ensures the AI creates a clean, catalog-ready image that fits online store layouts and brand requirements.
For example:
“a ceramic coffee mug on a white background, top-down angle, soft shadow, bright lighting, minimalist product photography style”
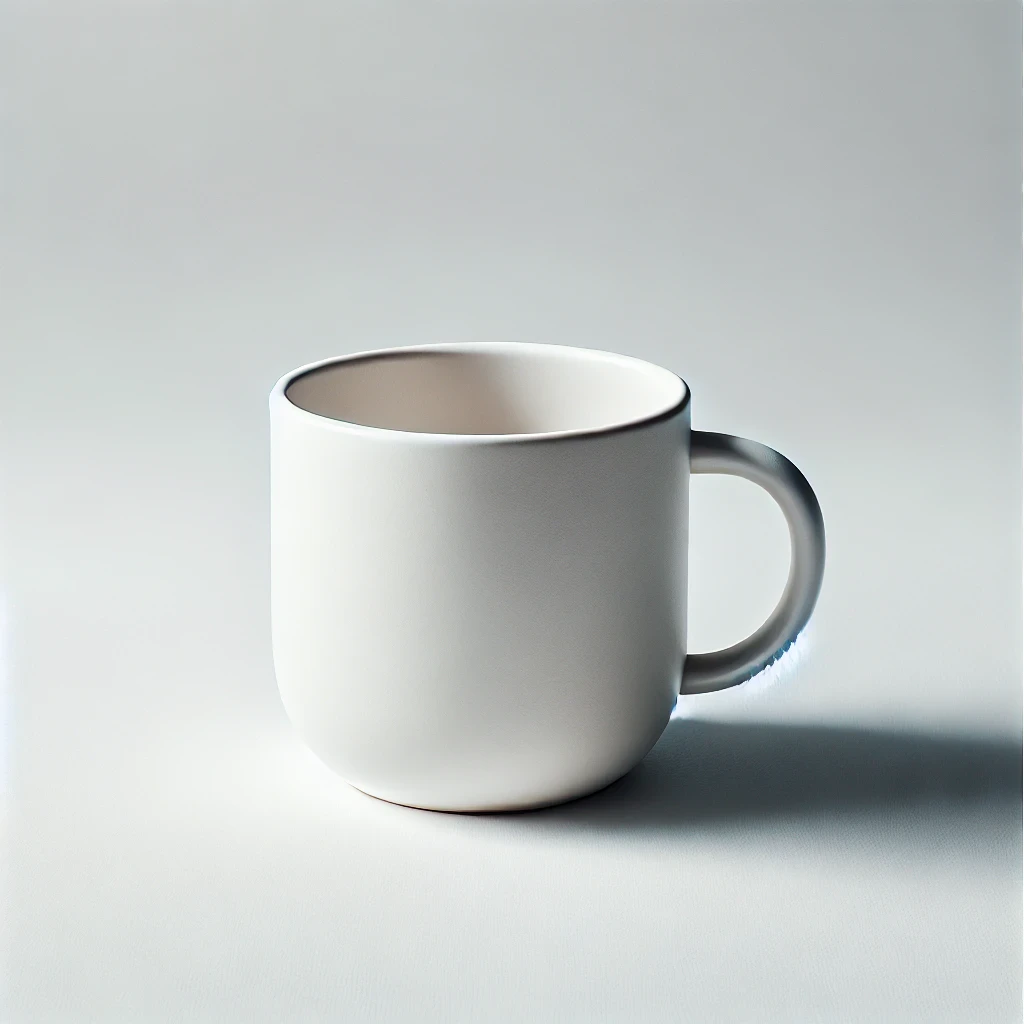

This prompt gives the AI clear directions for a standard product display. It matches what online customers expect to see in listings or ads.
AI tools like Adobe Firefly, Canva AI Image Generator, and DALL-E are commonly used to produce consistent eCommerce visuals. These tools speed up image creation and allow fast updates for seasonal, promotional, or color variations.
UI/UX Design Prompts: App Icons, Hero Images, and Splash Screens
AI-generated prompts help UI and UX designers create interface visuals like app icons, hero sections, and splash screens. These prompts focus on clarity, color balance, and alignment with the app’s theme.
A strong UI/UX prompt includes details about layout, shape, visual tone, and function. For app icons, it defines the icon’s form, color scheme, and style. For hero images and splash screens, it describes the scene, branding elements, and mood.
For example:
“a finance app icon, flat design, green and white color scheme, minimal style, scalable resolution”
This prompt helps generate an icon that fits both app stores and internal UI screens.

Designers use these prompts to speed up mockups, preview multiple ideas, and explore creative variations. Tools like Canva, MidJourney, and Figma AI Plugins allow direct integration of AI-generated visuals into digital product design workflows.
What Are the Most Popular Visual Styles in AI Image Generation?
AI models can create images in many different styles. Each visual style follows certain design rules, such as texture, color use, lighting, and shape. Users choose the style that fits their goal, whether it’s realistic, animated, or artistic.
The photorealistic style focuses on real-world detail. It uses sharp lighting, shadows, and textures to mimic real photography. This is often used for product mockups and lifestyle scenes.
Anime and comic styles feature bold outlines, flat colors, and expressive poses. These styles are popular for fan art, gaming avatars, and character-based designs.
Pixel art and retro styles recreate the look of old video games. These use low resolution, limited colors, and simple shapes. They’re used in indie game designs or vintage themes.
Abstract and artistic styles use soft textures, brush strokes, or surreal elements. Prompts with terms like “digital painting,” “oil style,” or “concept art” help generate these visuals.
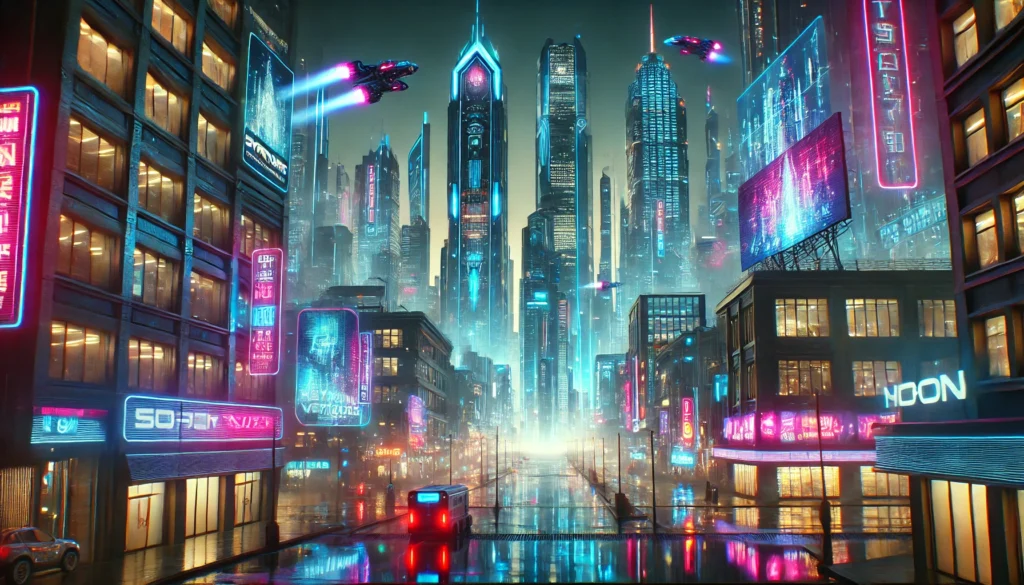
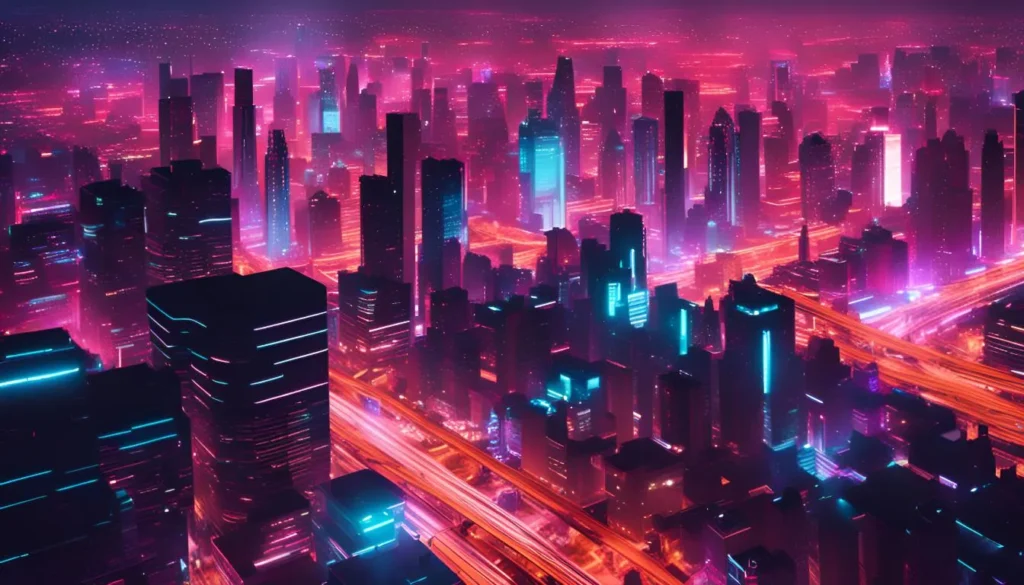
Cyberpunk and futuristic themes rely on neon colors, dark backgrounds, and tech-based design. They are often used in character art, urban scenes, or sci-fi branding.
For example:
“a city skyline at night, cyberpunk style, neon lights, dark background, cinematic lighting”
This prompt gives the AI clear visual instructions that shape the final image.
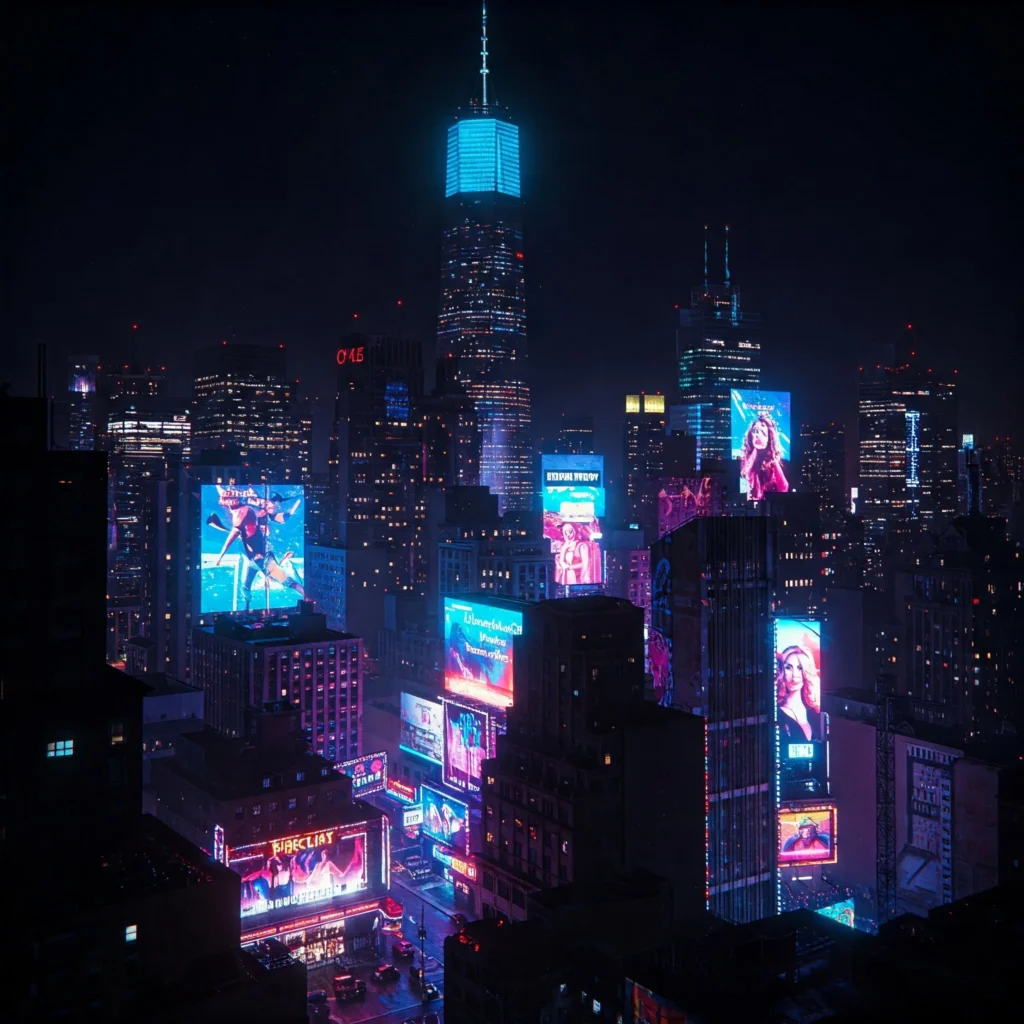

Tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E let users select or describe styles in the prompt to match the intended output.
Gaming & Fantasy (3D, Character Art)
AI-generated prompts for gaming and fantasy art are used to create 3D characters, magical creatures, and fantasy worlds. These prompts describe the character’s look, pose, armor, and setting. Designers use them for concept art, game development, and character exploration.
Fantasy prompts often include themes like “ancient forest,” “ice dragon,” or “battle-ready warrior.” 3D-related prompts add terms like “front view,” “ZBrush detail,” or “realistic textures” to guide the image.
For example:
“a female warrior in gold armor, standing in a ruined temple, fantasy setting, 3D style, front angle, dramatic lighting”
This prompt gives the AI all the details needed to create a strong character visual for fantasy games.
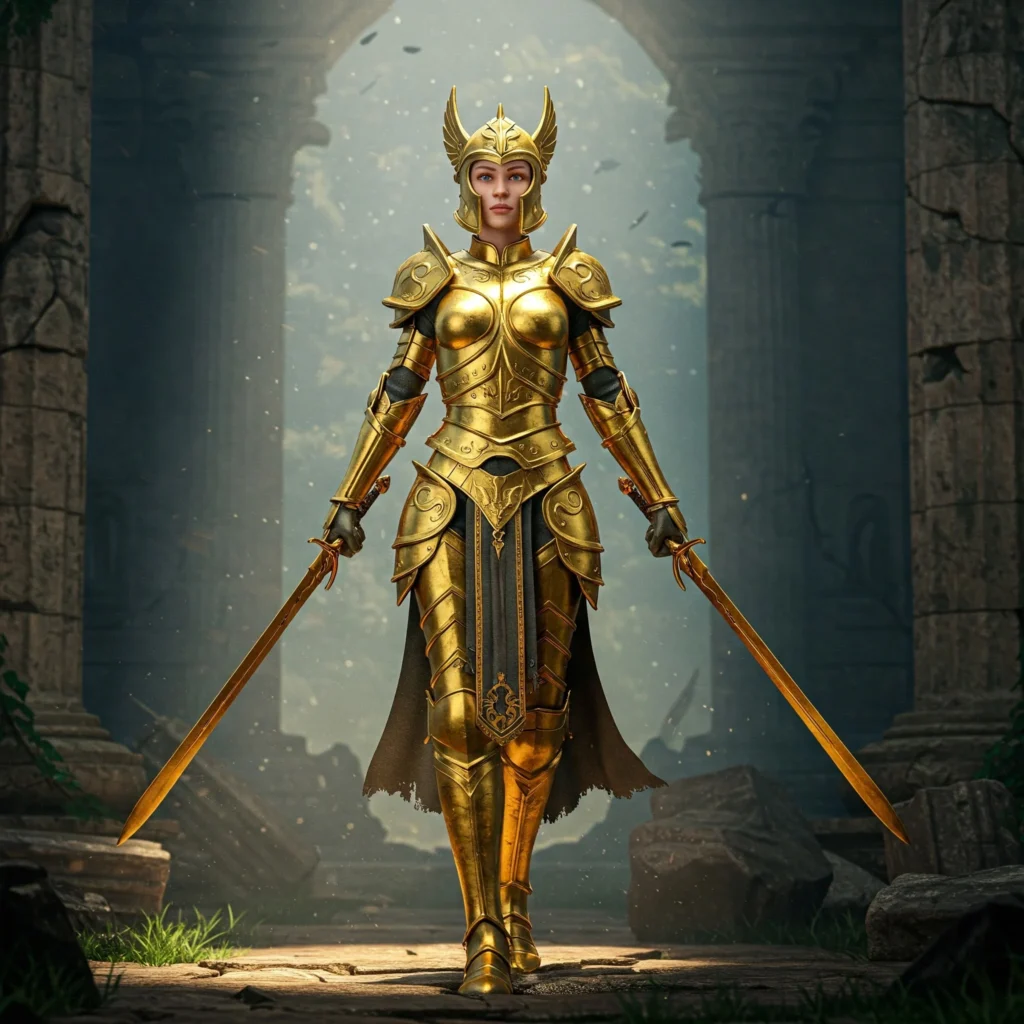

Tools like MidJourney, Leonardo AI, and Stable Diffusion help generate consistent outputs for 3D character design and fantasy world-building. These visuals support creative planning before full modeling or animation.
Photorealistic Images
Photorealistic image prompts are used to generate visuals that look like real photographs. These prompts include details such as lighting, shadows, surface texture, and camera angle to achieve lifelike results.
Photorealism is common in product mockups, interior visuals, food displays, and real-world scenes. These prompts aim to match real-life conditions, including lens type, focus depth, and environmental lighting.
For example:
“a glass of orange juice on a wooden table, morning sunlight, soft shadows, high resolution, photorealistic style”
This prompt gives the AI all the necessary visual cues to produce a natural, real-looking image.
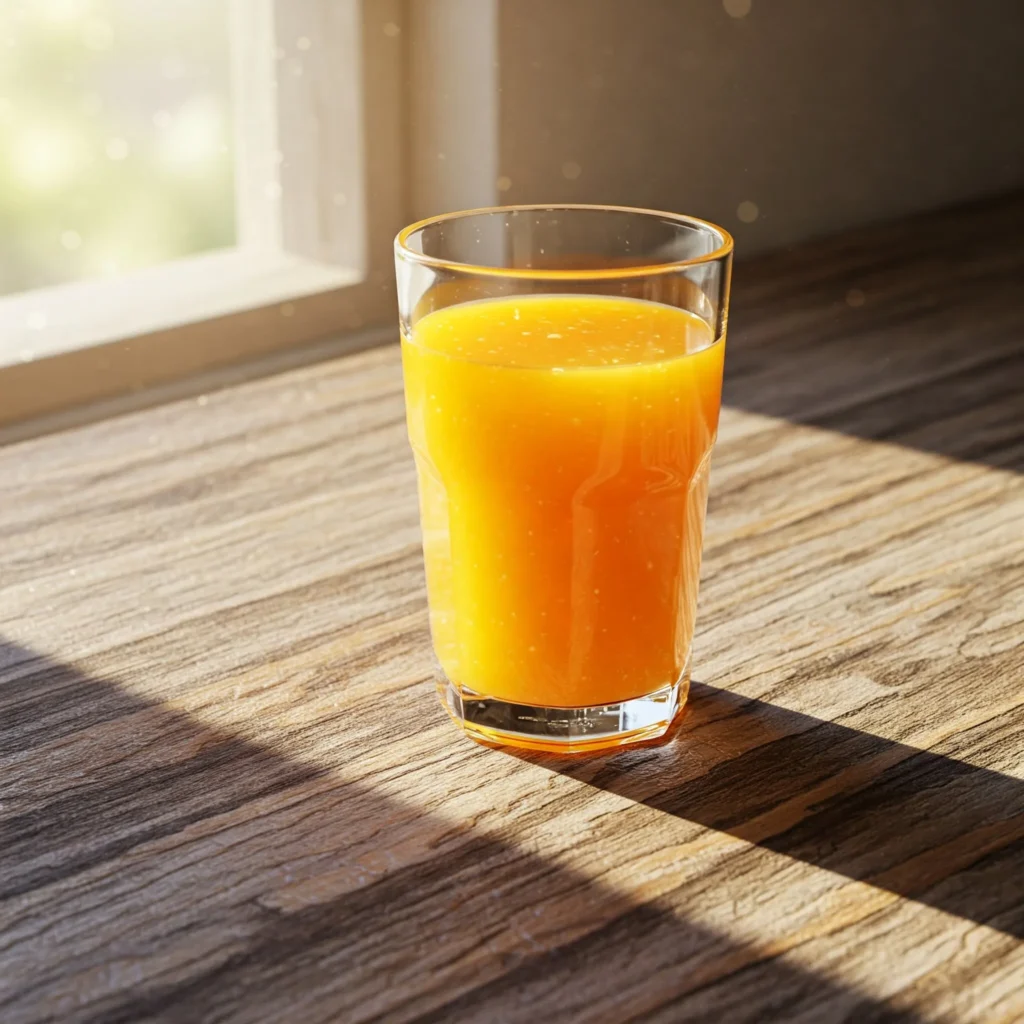

Tools like DALL-E, Adobe Firefly, and Stable Diffusion are often used to create photorealistic outputs for commercial use, e-commerce, and digital ads.
Anime & comic styles
Anime and comic styles are common formats in AI image generation. Anime prompts create visuals with big eyes, clean lines, and soft colors, similar to Japanese animation. Comic prompts generate images with bold outlines, high contrast, and dotted textures like Western comics.
Anime prompts often include terms like “anime style” or “cel-shading,” while comic prompts use words like “comic book style” or “halftone texture.” Each style responds well to modifiers like “sharp linework” or “bold shadows.”
Stable Diffusion, MidJourney, and DALL-E are popular tools for both styles. Models like Waifu Diffusion focus on anime, while MidJourney handles detailed comic and anime outputs. These styles are used in avatars, character art, fan art, and digital design.
Writing clear, specific prompts with the right style terms helps AI generate accurate results in either anime or comic style.
Abstract & artistic styles
Abstract and artistic styles in AI image generation create visuals based on emotions, colors, and forms instead of realistic details. Abstract prompts often use free shapes and strong contrasts, while artistic prompts follow styles like cubism or impressionism.
Common terms include “abstract painting,” “oil texture,” “modern art,” or “color splash.” These help the AI model understand the creative direction. Modifiers like “vivid contrast,” “grainy texture,” or “dreamlike shapes” improve the result.
Tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E support these styles. They’re useful for digital art, concept visuals, and mood boards.
Example:
“abstract color field, vivid red and blue, textured brushstrokes, modern art style”
This prompt generates an expressive, non-realistic image.

These styles focus on mood and artistic expression, not accuracy. Clear and specific prompts help AI produce the best results.
Pixel art & retro styles
Pixel art and retro styles in AI image generation focus on visuals that look like old video games or digital screens from the 80s and 90s. These styles use small pixels, limited color palettes, and simple shapes to create a nostalgic look.
Pixel art prompts include words like “8-bit,” “16-bit,” “low resolution,” or “arcade game sprite.” Retro styles often use terms like “CRT screen,” “vintage UI,” or “classic computer graphics.” These tell the AI to generate images with an old-school, digital feel.
Key attributes include blocky textures, bright colors, and visible pixel grids. Tools like Stable Diffusion and MidJourney are good at generating pixel-based or retro designs when given precise prompts.
These styles are commonly used in game design, NFT art, avatars, and creative posters. They’re ideal for projects needing a nostalgic or minimal look.
Example prompt:
“8-bit pixel art robot, bright primary colors, retro video game style, low resolution”
This creates a classic arcade-style character with simple pixel visuals.
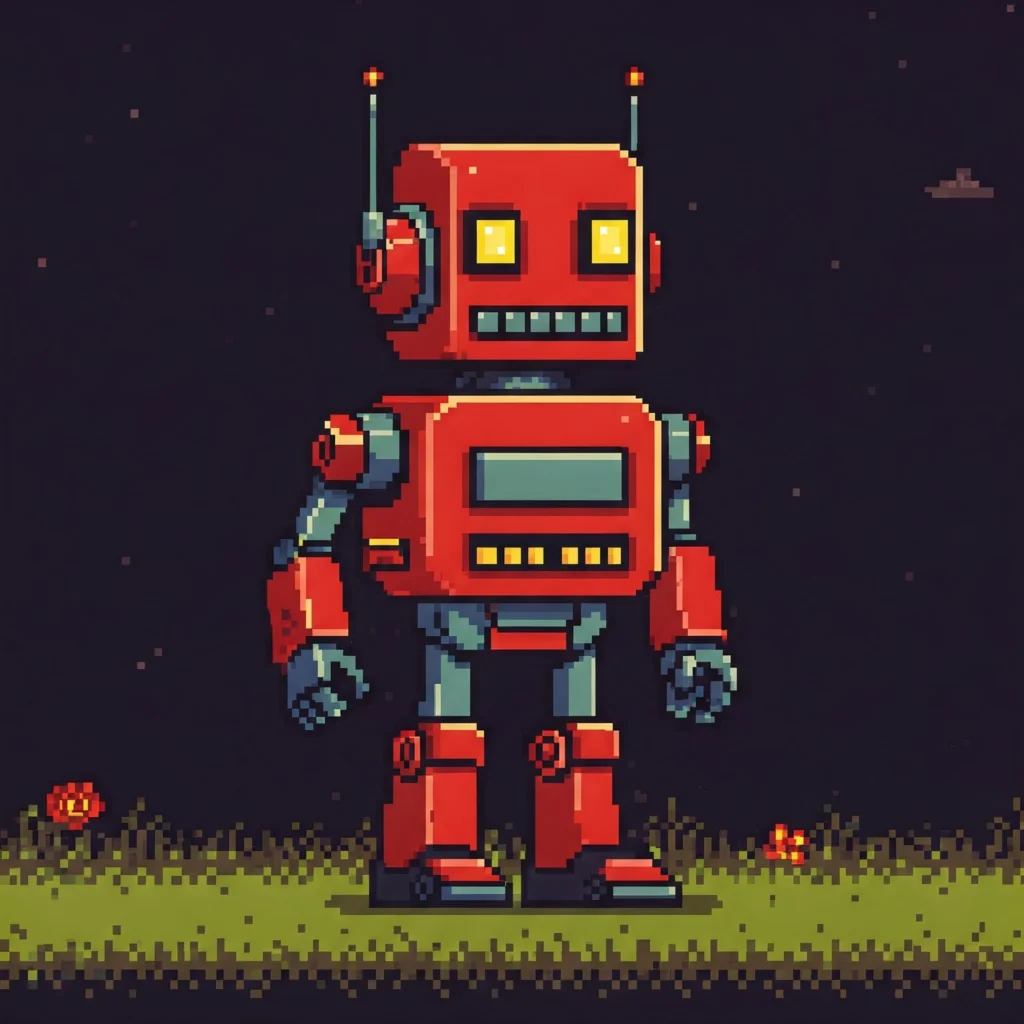
Pixel and retro prompts work best with clear style terms and visual modifiers. They’re not detailed or realistic but are effective for stylized, throwback designs.
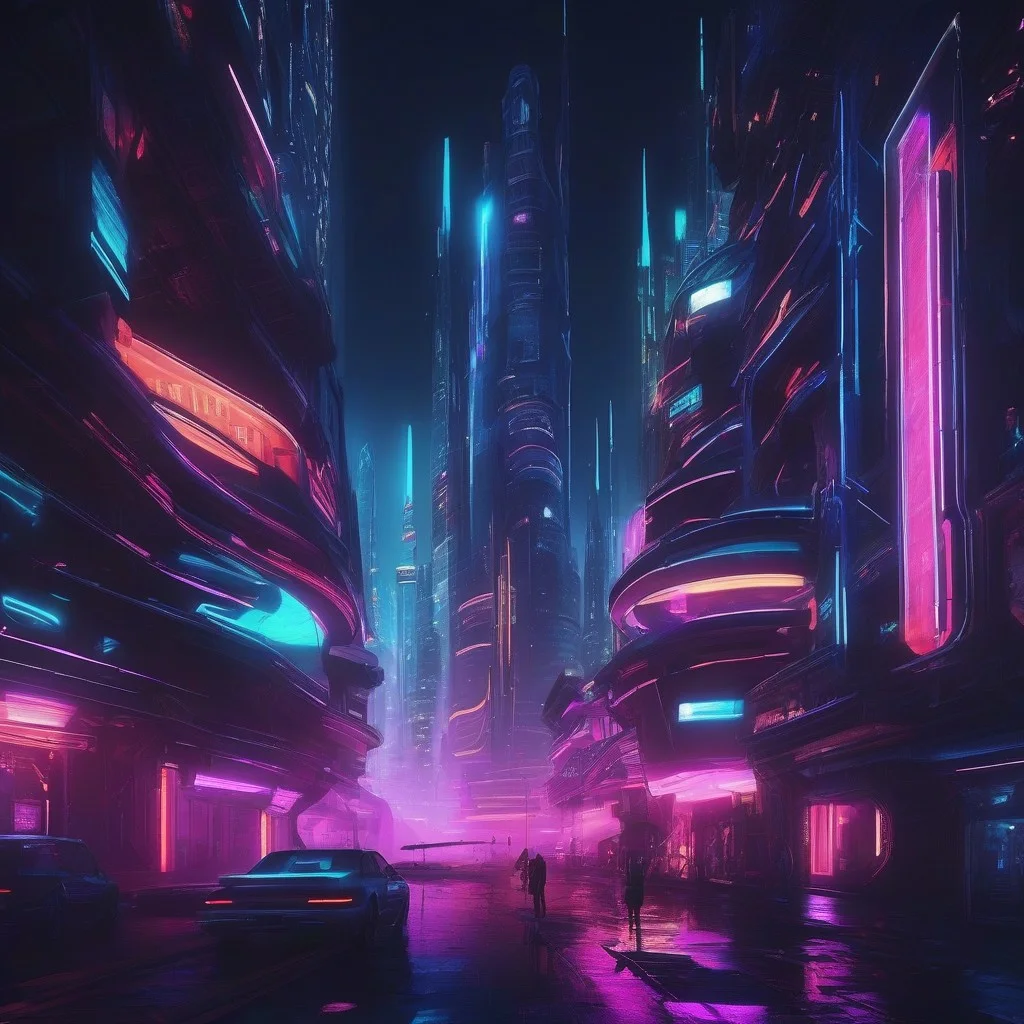
Cyberpunk aesthetics in AI-generated images
Cyberpunk aesthetics in AI-generated images show a dark, futuristic world with neon lights, high-tech cities, and dystopian themes. This style often includes cybernetic characters, glowing signs, rain-soaked streets, and a mix of advanced tech with urban decay.
Common prompt terms include “cyberpunk city,” “neon lighting,” “futuristic streetwear,” “high-tech slum,” and “sci-fi urban scene.” These help AI tools understand the visual style and mood. Related keywords like “synthwave,” “retrofuturism,” or “tech noir” are also useful.
Important attributes of cyberpunk prompts are deep shadows, reflective surfaces, bright neon colors, and crowded environments. Visual modifiers such as “purple-blue color palette,” “foggy atmosphere,” or “rain reflections” improve the image results.
AI tools like MidJourney and Stable Diffusion generate cyberpunk art well when prompts are specific. These images are used in gaming, digital art, concept scenes, and cinematic design.
Example prompt:
“cyberpunk alley, neon pink and blue lights, rainy night, futuristic signs, dystopian mood”
This creates a moody, high-tech street scene with clear cyberpunk features.
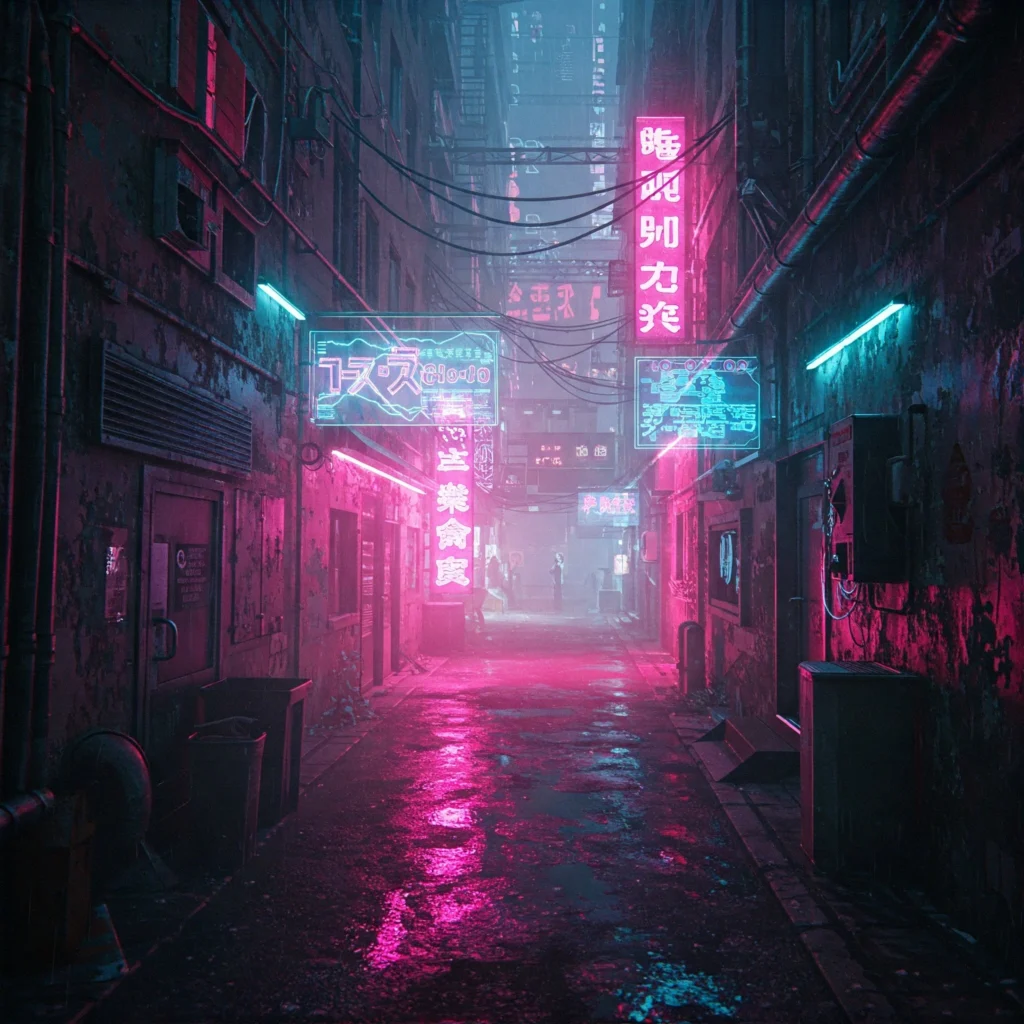

Cyberpunk prompts focus on contrast, lighting, and futuristic themes. Using clear style terms and visual details gives accurate, immersive images.
What Are the Best AI Tools for Image Generation?
The best AI tools for image generation use advanced models to turn text prompts into detailed visuals. These tools help users create art, product designs, characters, and more using simple text instructions.
| TOOL NAME | SPECIALITY | KEY FEATURES | BEST FOR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mid Journey | Artistic and cinematic images, high-resolution results with rich lighting and textures | Artistic, cinematic style, rich textures, and lighting | Artistic and cinematic imagery |
| Stable Diffusion | Full control with custom models, negative prompts, and fine-tuning, supports styles like photorealism, anime, and pixel art | Custom models, photorealism, anime, pixel art, negative prompts | Detailed control and custom model creation |
| Dall-E | Good for clean, concept-based images, follow natural language closely, and general-use visuals | Clean images, natural language prompts, general-use visuals | General-purpose visuals and concepts |
| Leonardo AI | Focuses on creative asset generation, supports fantasy art, characters, and game visuals with a high level of detail | Fantasy art, game visuals, high-detail character generation | Fantasy art and character/game design |
| Runway ML | Real-time editing, image-to-image generation, easy inpainting, good for creative workflows, and video content | Real-time editing, image-to-image generation, easy inpainting, good for creative workflows, and video content | Creative workflows and video content |
[INSERT COLLAGE]: 5 small images from 5 tools
Each tool works better for certain styles. Choosing the right one depends on the project goal, output quality, and control options. Clear, descriptive prompts help any tool perform better.
How Do Major Text-to-Image Tools Compare in Accuracy?
Text-to-image tools differ in how accurately they follow the user’s prompt. The main tools, MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, Dall-E, Artbreeder, Leonardo AI, and Runway ML, have different ways of understanding and turning text into visuals.
Strengths: Known for producing visually striking results that excel in creativity and artistic expression, interprets abstract prompts well.
Accuracy in Following Prompts: MidJourney tends to prioritize artistic flair and visual appeal over literal accuracy. It captures the essence of creative prompts but may deviate from the strict details of the text.
Best For: Those looking for visually appealing, stylistic, and mood-driven imagery. Ideal for artists and designers focused on creative concepts rather than literal accuracy.
Limitations: While visually stunning, MidJourney might not accurately follow every detail of the prompt and can sometimes prioritize style over content.
Resolution Support: High resolution support for detailed, cinematic visuals.
Speed of Generation: Moderate speed; generates images with heavy creative processing.
Use Cases: Great for concept art, visual art, and creative pieces. Best for designers and visual artists who focus on mood and aesthetic.
Strengths: Provides comprehensive control over prompts with advanced features such as negative prompts, prompt weights, and aspect ratio adjustments for fine-tuning.
Accuracy in Following Prompts: Stable Diffusion stands out for offering a balanced approach between accuracy and creative control. It allows fine-tuning with modifiers like negative prompts and weights, leading to more customizable results.
Best For: Professionals or hobbyists who need both accuracy and creative flexibility. Suitable for technical projects requiring fine adjustments and users seeking detailed control.
Limitations: Stable Diffusion’s learning curve can be steeper due to the many adjustable features. However, it can be overwhelming for new users seeking quick results.
Resolution Support: Supports a wide range of resolutions, including high-definition outputs.
Speed of Generation: Moderate to fast speed depending on settings and model size.
Use Cases: Highly versatile for various tasks, including photorealism, gaming, and concept art. Ideal for professionals needing detailed control.
Strengths: Strong understanding of specific instructions, produces clear and literal representations of text prompts with high fidelity.
Accuracy in Following Prompts: DALL-E excels at interpreting and creating precise, literal representations of prompts, which is ideal for users who require direct, clear results. However, its output may lack stylistic nuance or artistic depth.
Best For: Users who need exact and literal renditions of their prompts without much artistic modification. Suitable for tasks requiring accuracy in depiction.
Limitations: Lacks the flexibility to modify or tweak styles beyond the text input. Struggles with more abstract or non-literal prompts.
Resolution Support: Supports resolutions suitable for most general use cases, not as high as others.
Speed of Generation: Fast and efficient, especially for simple and concept-based tasks.
Use Cases: Best for concept design, marketing materials, and general-use imagery. Excellent for clear, literal visuals.
Strengths: Focuses on blending and evolving images with user input. Known for its ability to create and manipulate portraits and landscapes.
Accuracy in Following Prompts: Artbreeder allows users to evolve images based on blending and genetic algorithms, but it is less focused on strict prompt following and more on image evolution.
Best For: Artists and creators looking to evolve and manipulate images interactively. Perfect for blending concepts and working with existing images.
Limitations: Artbreeder’s evolution of images can be unpredictable and may not always yield the desired result. Less focus on prompt-based generation.
Resolution Support: Resolution support varies based on the complexity of the blend, but generally provides good quality results.
Speed of Generation: Fast for interactive editing and evolving images, but slower for highly complex generations.
Use Cases: Excellent for creative experimentation, character creation, and portrait art. Great for users interested in creative and iterative processes.
Strengths: Real-time editing capabilities, image-to-image generation, inpainting, and video content creation, useful for dynamic and creative workflows.
Accuracy in Following Prompts: Runway ML offers flexibility with real-time editing and image-to-image generation, but its accuracy in prompt adherence depends on the adjustments made during the editing process.
Best For: Creative professionals working on dynamic projects involving both still images and video. Best for workflows requiring quick iterations and real-time adjustments.
Limitations: Runway ML’s output depends on manual adjustments, and while it excels in editing, the generation from prompts can vary depending on user input and workflow.
Resolution Support: Supports high resolutions for video and image editing tasks.
Speed of Generation: Fast and versatile for video and interactive projects.
Use Cases: Highly flexible, excellent for creative video and content workflows. Best for video producers and interactive media creators.
Strengths: Creative asset generation, especially for detailed fantasy art and characters.
Accuracy in Following Prompts: Leonardo AI is highly effective for generating precise, imaginative, and detailed fantasy characters, artworks, and game assets based on user input.
Best For: Generating fantasy art, character design, and game assets with an emphasis on high detail and creativity.
Limitations: May require specific prompts for optimal results, particularly when creating characters or scenes with complex backstories.
Resolution Support: High resolution support for detailed and intricate designs.
Speed of Generation: Moderate speed; great for creating high-detail art but can be slower with more complex designs.
Use Cases: Excellent for fantasy artwork, character development, and game asset generation. Best suited for artists creating immersive worlds.
Accuracy in image generation means how well the output matches the text input. Each tool has strengths. The best choice depends on whether you need literal results, artistic output, or technical control.
How Can AI Be Used for Image Editing and Enhancement?
AI-powered image editing is the process of changing or improving digital images using artificial intelligence tools like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, or Runway ML. Unlike traditional software such as Adobe Photoshop, which needs manual input.
AI uses generative models, diffusion techniques, and neural networks to edit images automatically. With simple text prompts, users can ask the AI to do things like fill in missing parts (inpainting), extend an image (outpainting), replace backgrounds, change styles, or remove objects.
These tools work through text-to-image, image-to-image, or prompt-to-image systems, and understand instructions using text embeddings and prompt conditioning.
This kind of editing, also known as generative fill, smart editing, or AI-assisted photo retouching, is especially useful for designers, e-commerce sellers, content creators, and digital artists who need fast and flexible ways to create and edit visuals.
What are the key image editing techniques used in AI?
AI-powered image editing includes a variety of intelligent techniques. These techniques rely on generative models and deep neural networks to enhance or modify images based on prompt input. Prompt conditioning to understand what the user wants and create high-quality visual results.
- Inpainting (Filling Missing Parts)Also known as smart fill or prompt-based image repair, inpainting helps AI fill in damaged or blank parts of an image by looking at nearby pixels and the overall scene.
Example: If part of a person’s face is scratched in an old photo, AI can restore it to look complete again. - Outpainting (Extending an Image)
Outpainting, also known as image extrapolation or canvas expansion, enables AI to extend an existing image beyond its original frame while preserving style and content coherence.
Example: Suppose you have a portrait cropped at the shoulders. Outpainting can be used to expand the image downward, generating the rest of the body and even the background in a seamless manner. - Background Replacement
AI separates the background from the main subject using semantic segmentation and allows you to change it. Also known as scene swapping or backdrop editing.
Example: Turn a plain studio shot into a beach scene just by prompting “replace background with sunset at the beach.” - Face Restoration
Also called facial enhancement, AI portrait fixing, or photo restoration, this technique improves blurry, low-resolution, or damaged facial features using pre-trained facial recognition models like GFPGAN or CodeFormer.
Example: A pixelated photo of a grandparent from the 1950s can be cleaned up with AI to show sharper eyes, smoother skin, and more defined facial contours. - Style Transfer
Known as art style blending or visual styling, this lets you apply an art style from one image to another, like converting a photo into a painting.
Example: Transform your landscape photo into a Studio Ghibli-style scene, with soft, vibrant colors and whimsical details inspired by films like Spirited Away. - Object Removal or Swapping
This technique, also called AI erasing, semantic masking, or visual cleanup, removes or changes unwanted items in a scene.
Example: You can remove a trash can from a street scene by simply masking it and prompting the AI to “replace with pavement,” and it will generate a seamless result as if the object was never there.
Top 10 AI Tools to Support Image Editing with Prompts?
AI image editing tools let you change or improve images just by typing what you want. These tools use generative AI, diffusion models, and smart visual algorithms to understand your instructions.
If you want to remove an object, fix a face, or change a background, you can do it using text prompts.
1. Adobe Firefly
Adobe Firefly, part of Photoshop and Express, lets you use simple prompts like “remove background” or “add sky” to edit images. It supports Generative Fill, inpainting, and object replacement, making it perfect for designers and marketers.
2. DALL-E by OpenAI
DALL-E 2 and DALL-E 3 can edit, expand, or fix images with natural language. You just describe what you want, and the tool makes it happen using diffusion techniques and CLIP-based prompt understanding. It’s available inside ChatGPT Pro.
3. Runway ML
Runway ML is an easy-to-use platform where you can remove backgrounds, fill in missing parts, and apply styles using either text prompts or simple tools. It supports Stable Diffusion and is great for video editors and creatives.
4. Stable Diffusion (AUTOMATIC1111, Clipdrop, etc.)
Stable Diffusion supports powerful image editing features like inpainting, depth-based edits, style transfer, and more. Tools like AUTOMATIC1111, ComfyUI, and Clipdrop let users control every detail with custom workflows.
5. Canva AI (Magic Edit)
Canva’s Magic Edit lets you add or remove objects, change styles, and enhance visuals using prompts. It’s very popular for social media posts, ads, and business graphics.
6. PhotoRoom
PhotoRoom is made for product photography. It can remove backgrounds, add shadows, and even change settings (e.g., “place on marble table”), all with text prompts. Perfect for eCommerce sellers.
7. Fotor AI Editor
Fotor has tools like AI Retouch, Object Remover, and Background Eraser. It’s designed for quick edits by influencers, bloggers, and small business owners, with prompt-based controls.
8. Picsart AI
Picsart has features like AI Replace, AI Background, and AI Eraser, allowing users to edit images with natural language. It’s great for mobile content creators and TikTok users.
9. Playground AI
Playground AI lets you experiment with Stable Diffusion and DALL-E to edit images using prompts. It’s easy to use and great for beginners, students, and prompt engineers.
10. Artbreeder
Artbreeder uses sliders and text input to edit things like faces, landscapes, or anime art. It works through GANs and genetic-style mixing, helping users control image features like age, color, or mood.
How to Write Prompts for Editing Existing Images?
To edit existing images with AI, you can write simple text prompts that tell the AI what to change. AI Tools understand these instructions and apply edits using techniques like inpainting, image-to-image editing, or mask-based changes.
You just upload an image, highlight the part you want to change, and describe what you want, for example, “remove the chair” or “change the sky to sunset.” Good prompts include clear object names, the action (like add, remove, or change), and optional details like color, style, or texture.
This is called prompt-based editing, also known as AI retouching, generative fill, or semantic photo editing, and it’s used for everything from fixing portraits to creating new marketing visuals.
Here are some prompt templates that work across above above-given list of tools
- Object removal + scene completion
“Remove the person in the background and fill with beach sand.”
- Background replacement + light adjustment
“Replace the cloudy sky with a sunset.”
- Clothing change using a prompt-based overlay
“Add a black leather jacket on the person.”
- Style transfer + aesthetic filter
“Make the image look like a 90s film photo with grainy texture.”
- Face restoration using portrait enhancement models
“Fix the blurry face and enhance eye details.”
- Outpainting + urban scene generation
“Extend the image to the left with a matching cityscape.”
Comparative Analysis of Image Generation Models
Different AI models generate images in unique ways. A comparative analysis helps understand how each model performs in terms of accuracy, style, control, and flexibility. The main models are MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, Artbreeder, Runway ML, and Leonardo AI.
MidJourney
Focus: Artistic quality, strong lighting, creative textures, and visually rich results
Best For: Artistic and visually rich results with mood and style instructions
Strengths: Creates vivid, dramatic visuals with a focus on mood and lighting
Limitations: Focuses more on artistic aspects, sometimes at the expense of literal accuracy
Resolution Support: High resolution support for detailed, cinematic visuals
Model Type: Transformer model, focused on artistic generation
Speed of Generation: Moderate speed; generates images with heavy creative processing
Ease of Use: Easy to use, especially for users focused on visual art and creativity
Flexibility in Use Cases: Great for concept art, visual art, and creative pieces
Stable Diffusion
Focus: High control, fine-tuning with custom models, negative prompts, prompt weights, and aspect ratios
Best For: Precise control over output with customizable settings for both stylized and realistic images
Strengths: Balances control and creative flexibility, suitable for detailed, realistic, or stylized images
Limitations: Learning curve for adjusting detailed settings, which may overwhelm new users
Resolution Support: Supports a wide range of resolutions, including high-definition outputs
Model Type: Diffusion model, offering fine control and versatility
Speed of Generation: Moderate to fast speed depending on settings and model size
Ease of Use: Moderately difficult; requires familiarity with advanced settings for best use
Flexibility in Use Cases: Highly versatile for various tasks, including photorealism, gaming, and concept art
DALL-E
Focus: Interprets natural language well, generates clean, concept-based images
Best For: General tasks requiring clean, clear, and concept-driven visuals
Strengths: Ideal for generating clean, accurate images that adhere closely to the prompt
Limitations: May not offer as much artistic depth or creativity compared to other models
Resolution Support: Supports resolutions suitable for most general use cases, not as high as others
Model Type: Transformer model, highly effective at understanding natural language
Speed of Generation: Fast and efficient, especially for simple and concept-based tasks
Ease of Use: Very user-friendly with intuitive natural language-based input
Flexibility in Use Cases: Best for concept design, marketing materials, and general-use imagery
Artbreeder
Focus: Blending and evolving images with user input
Best For: Artists and creators looking to evolve and manipulate images interactively
Strengths: Allows for evolving images from genetic algorithms and blending concepts
Limitations: Less focus on prompt-based generation, unpredictable results
Resolution Support: Resolution support varies based on the complexity of the blend
Model Type: Generative model, focused on blending images and creating new ones
Speed of Generation: Fast for interactive editing and evolving images, but slower for highly complex generations
Ease of Use: Easy to use with simple controls, but blending images can be trial and error
Flexibility in Use Cases: Excellent for creative experimentation, character creation, and portrait art
Runway ML
Focus: Real-time editing capabilities, image-to-image generation, inpainting, and video content creation
Best For: Creative professionals working on dynamic projects involving both still images and video
Strengths: Real-time editing, inpainting, and strong integration with video workflows
Limitations: Output depends on manual adjustments, workflow can be inconsistent
Resolution Support: Supports high resolutions for video and image editing tasks
Model Type: Combines elements of transformers and GANs for both real-time and generative tasks
Speed of Generation: Fast and versatile for video and interactive projects
Ease of Use: Moderately easy to use, especially for users with video or design experience
Flexibility in Use Cases: Highly flexible, excellent for creative video and content workflows
Leonardo AI
Focus: Creative asset generation, especially for detailed fantasy art and characters
Best For: Generating fantasy art, character design, and game assets
Strengths: High attention to detail and quality in creating immersive, fantastical visuals
Limitations: May require specific prompts for optimal results in certain genres
Resolution Support: High resolution support for detailed and intricate designs
Model Type: Generative model, highly focused on creative, character-driven art
Speed of Generation: Moderate speed; great for creating high-detail art but can be slower with more complex designs
Ease of Use: User-friendly with presets and guidance for artists
Flexibility in Use Cases: Excellent for fantasy artwork, character development, and game asset generation
Example test prompt:
“futuristic cityscape at night, neon lights, cinematic view”
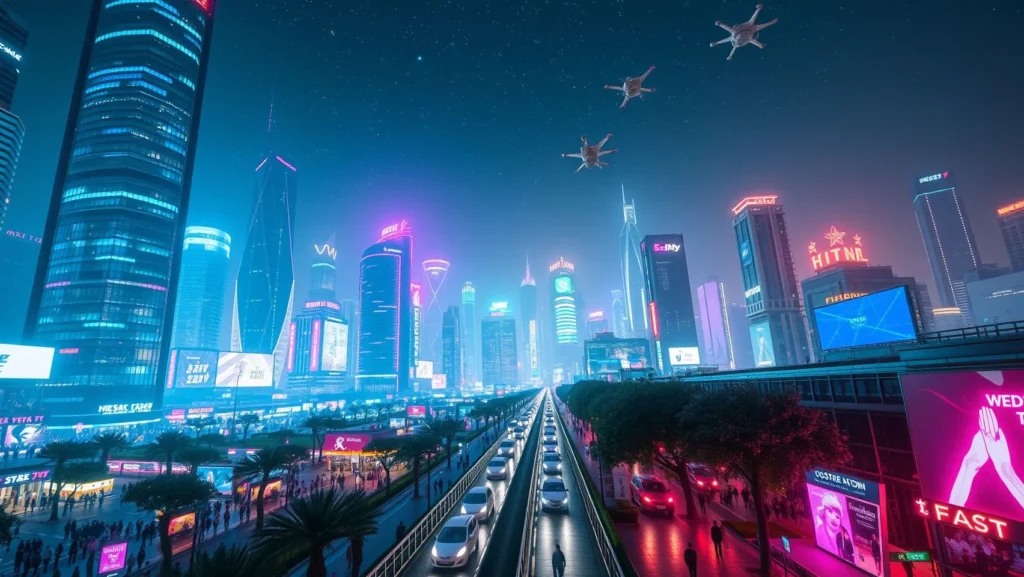
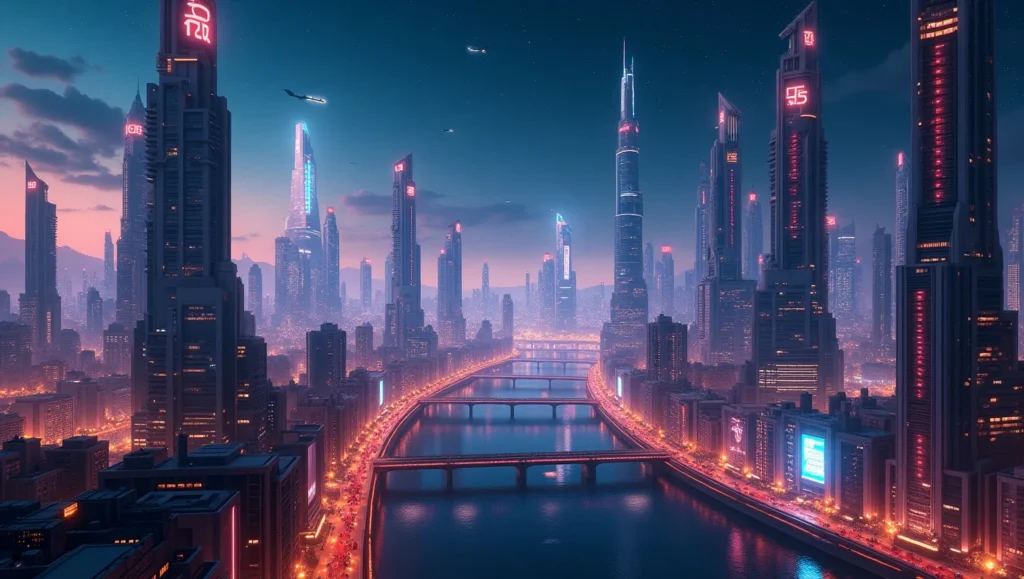






MidJourney creates a dramatic scene, Stable Diffusion adds control options, and DALL-E focuses on object accuracy.
Choosing the right model depends on project needs, creative visuals, controlled output, and clear prompt matching. Understanding these models helps users write better prompts and get better images.
What Are the Differences in Prompt Structures Between DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion?
Each AI tool uses a different structure for writing prompts. DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion interpret the text differently, so prompt format and wording affect results.
- DALL-E works best with full sentences and natural language. It focuses on clarity and object accuracy. You can describe a scene as telling a story.
Example: “A cat sitting on a windowsill with a sunset in the background” - MidJourney prefers short, style-focused phrases. It responds well to keywords like lighting, texture, camera angle, and color. Prompts often skip grammar and focus on visual modifiers.
Example: “cat, windowsill, sunset, cinematic lighting, soft shadows, 8k” - Stable Diffusion allows more control. You can use commas to separate concepts, weights to guide importance, and even negative prompts to remove unwanted elements.
Example: “cat on the windowsill, sunset light, cinematic style, (sharp focus: 1.2), (blurred background), –no water”
Prompt structure affects how well the AI understands the subject, style, and focus. DALL-E is best for simple concepts, MidJourney for artistic detail, and Stable Diffusion for technical control.
Knowing how to write for each model helps users get better, more accurate images.
How Do Stable Diffusion and MidJourney Handle Negative Prompts?
Negative prompts tell the AI what to avoid in the image. Stable Diffusion and MidJourney handle negative prompts in different ways.
- Stable Diffusion supports direct negative prompts. You can list what should not appear. This helps filter out unwanted elements like extra limbs, low quality, or incorrect lighting. Users can also assign weights to control how strongly the model avoids these elements.
- MidJourney does not use traditional negative prompts. Instead, users reduce unwanted features by adjusting the main prompt. Users write more focused and clear positive prompts to avoid certain styles or objects. MidJourney may also respond to styling terms like “clean” or “realistic” to guide image direction.
Show a before/after example right after you mention “Stable Diffusion supports negative prompts while MidJourney doesn’t.”
Side‑by‑side, generated from the same base prompt, Midjourney pushes the palette toward warm peaches and golds, while Stable Diffusion remains neutral because the added negative weight, over-saturated colors: -1 – suppresses that excess warmth.
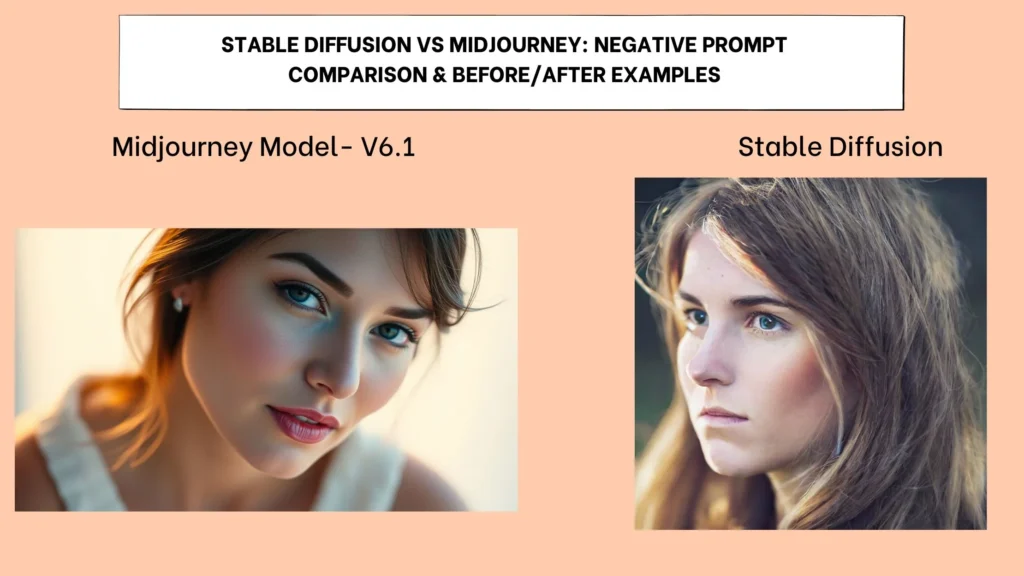
Example:
“portrait of a woman, soft lighting, sharp focus, –no blurry face, –no double eyes”
Prompt control in Stable Diffusion is more technical and flexible. MidJourney relies on a strong keyword balance to reduce unwanted results.
Using a clear prompt structure and accurate descriptors helps both tools produce better images with fewer errors or distractions.
How Accurate Are AI Models Like DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion in Interpreting User Prompts?
AI models like DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion vary in how accurately they understand and follow user prompts. Each model has a different way of processing keywords, styles, and object details.
- DALL-E focuses on language understanding. It interprets full sentences and descriptive phrases well. It works best for basic concepts and clearly described objects.
- MidJourney responds more to artistic and visual keywords. It gives strong output for style, lighting, and mood, but sometimes adds or changes small elements.
- Stable Diffusion offers detailed control. It can follow prompts with modifiers, weights, and exclusions to generate more accurate images.
Accuracy depends on how clearly the prompt defines the subject, style, and structure. DALL-E is strong indirect meaning. MidJourney is better at artistic mood. Stable Diffusion allows fine-tuned adjustments.
Example prompt:
“a fantasy castle on a mountain, sunset lighting, ultra-realistic, wide-angle view”

This image compares three AI models: DALL-E nails the situation with simple textures; MidJourney adds vibrant sunset colors and dramatic shadows; and Stable Diffusion provides clear architectural detail with fine wall sharpness and adjustable sky elements.
DALL-E may place the castle correctly, but with plain detail. MidJourney may add dramatic lighting. Stable Diffusion lets users adjust focus and sharpness or remove sky elements.
How Do AI Models Approach Prompting Attributes Such as Weighting, Negative Prompts, Image Resolution, and Aspect Ratio Control?
AI models use different methods to manage prompt attributes like weighting, negative prompts, image resolution, and aspect ratio. These features help users control image quality, structure, and unwanted elements.
Weighting allows users to give more importance to certain words in a prompt. For example, in Stable Diffusion, adding values like (sharp focus:1.5) tells the model to make that detail stronger. MidJourney doesn’t use exact weights but responds to word order and emphasis. DALL-E doesn’t support weighting.
Negative prompts remove unwanted elements. Stable Diffusion supports them directly using no structured phrases. MidJourney requires rewriting prompts to avoid unwanted parts. DALL-E has limited support for this feature.
Image resolution control is strong in Stable Diffusion, where users can set pixel size manually. MidJourney offers predefined quality settings like quality and upscale tools. DALL-E automatically adjusts the resolution and has less manual control.
The aspect ratio helps shape the image frame. In MidJourney, you can use ar 16:9 or ar 1:1. Stable Diffusion allows setting height and width directly. DALL-E offers fixed aspect ratios depending on the prompt and output type.
Example prompt for Stable Diffusion:
“sci-fi city at night, neon lights, (high detail:1.4), 1024×768”
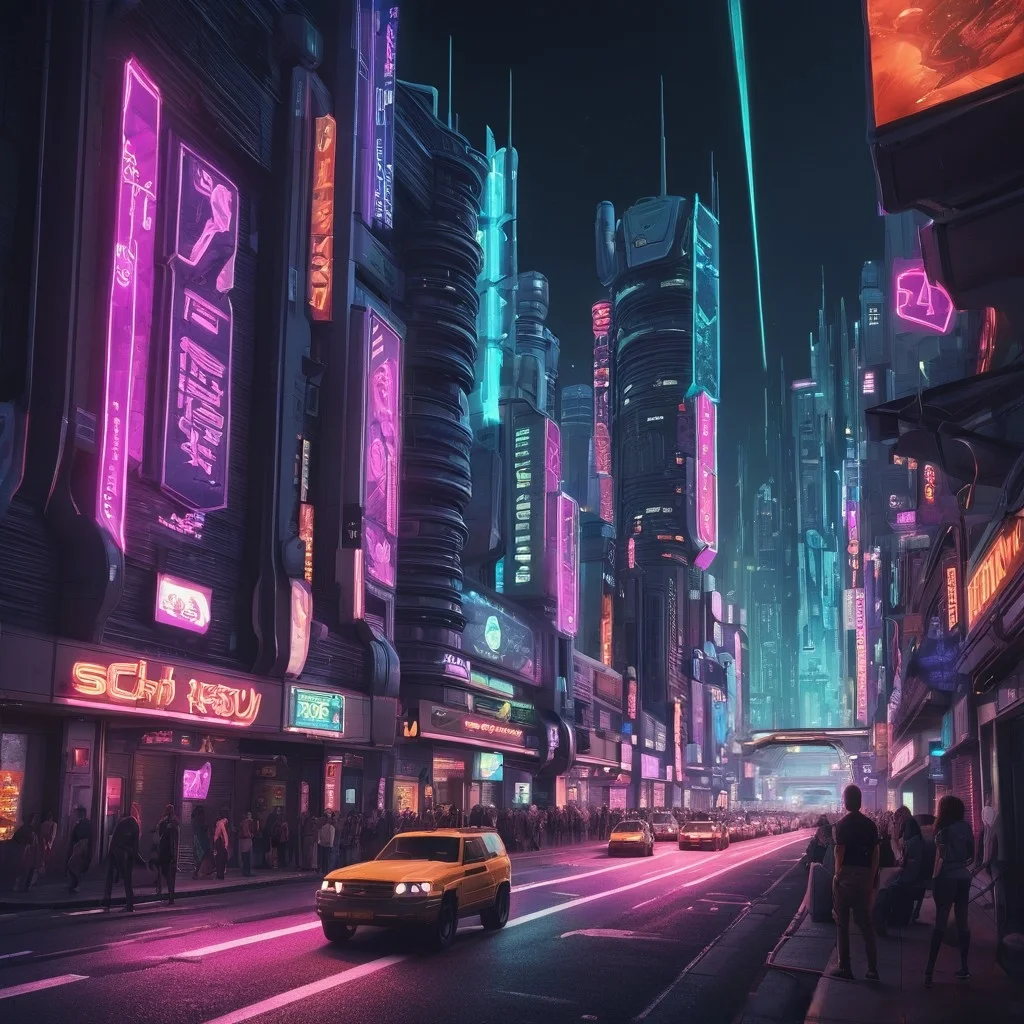

Choosing the right attributes helps generate better, cleaner, and more targeted images. Each model has different levels of prompt control, and using these features correctly improves the final output.
How Does MidJourney Perform in Producing Hyper-Realistic Versus Artistic Image Outputs?
MidJourney can create both hyper-realistic and artistic images, depending on how the prompt is written. The model is known for its strong visual style, lighting effects, and detailed textures.
For hyper-realistic outputs, MidJourney performs well with prompts that include words like “photo-realistic,” “real lighting,” “natural texture,” or “sharp focus.” These terms help guide the model toward life-like images.
For artistic results, it responds to style-based prompts using words like “watercolor,” “oil painting,” “concept art,” or “digital illustration.” Artistic prompts often have strong colors, surreal features, or imaginative shapes.
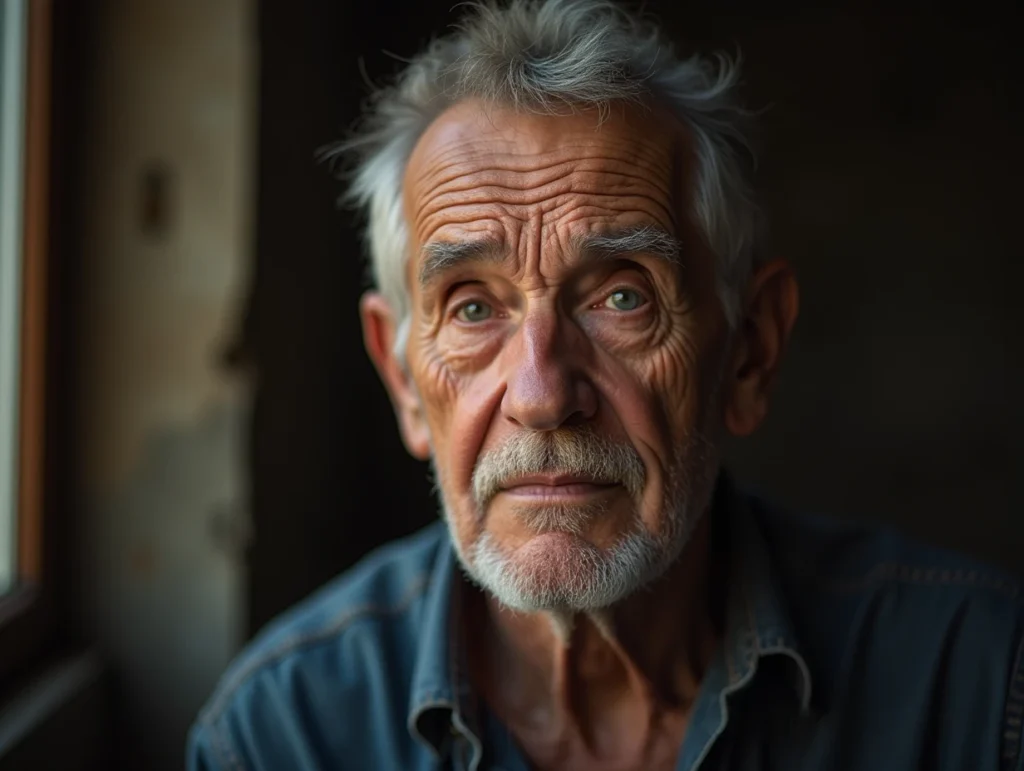
Example of a hyper-realistic image:
“portrait of an old man, photo-realistic, sharp details, natural lighting, 85mm lens”

Example for artistic image:
“portrait of an old man, oil painting style, brush strokes, warm tones, dramatic lighting”
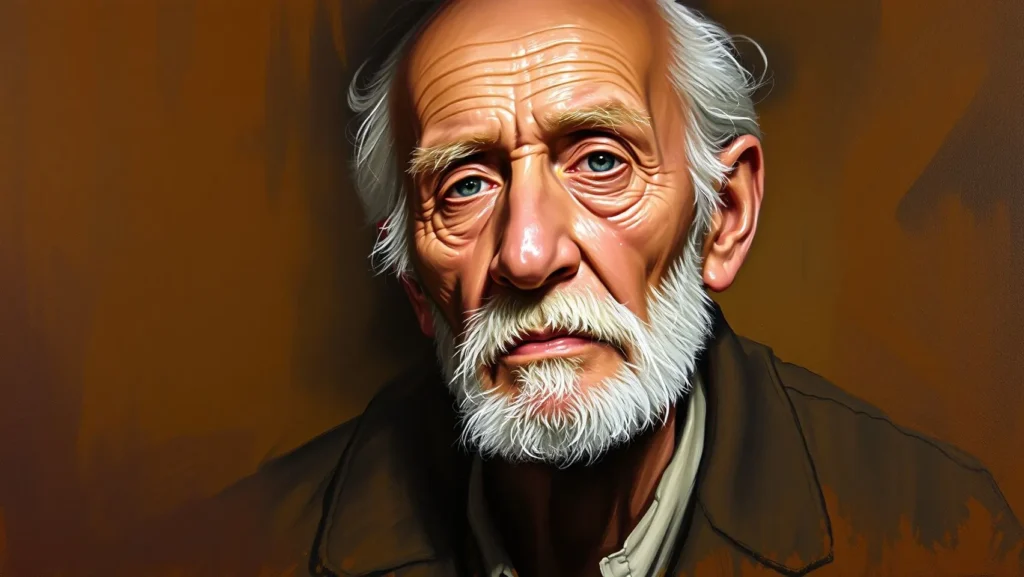

MidJourney leans slightly more toward artistic output by default. However, with the right visual keywords, it can balance between realism and stylization.
Using specific terms for either photo quality or art style helps MidJourney produce the desired look with better accuracy.
How Does Image Structure Control Differ Between Stable Diffusion and DALL-E?
Image structure control refers to how much a user can shape the generated image’s layout, composition, and design. Stable Diffusion and DALL-E offer different levels of control in this area.
- Stable Diffusion gives high control. Users can adjust the structure using aspect ratios, prompt weights, and custom settings. It supports techniques like inpainting (editing parts of an image) and control networks that guide image layout with more precision.
- DALL-E focuses on simplicity. It works with natural language and creates images based on full-sentence prompts. While it understands layout-related instructions, it doesn’t offer deep structural editing or prompt weighting like Stable Diffusion.
Stable diffusion is better for complex image structures or detailed compositions. It allows manual size control, object positioning, and image-to-image features. DALL-E is easier for basic scenes and direct concepts.
Example using Stable Diffusion:
“a garden with a fountain in the center, (symmetrical layout), soft focus background, –ar 3:2”

Example using DALL-E:
“A garden with a central fountain and flowers around it, in a soft, balanced layout.”
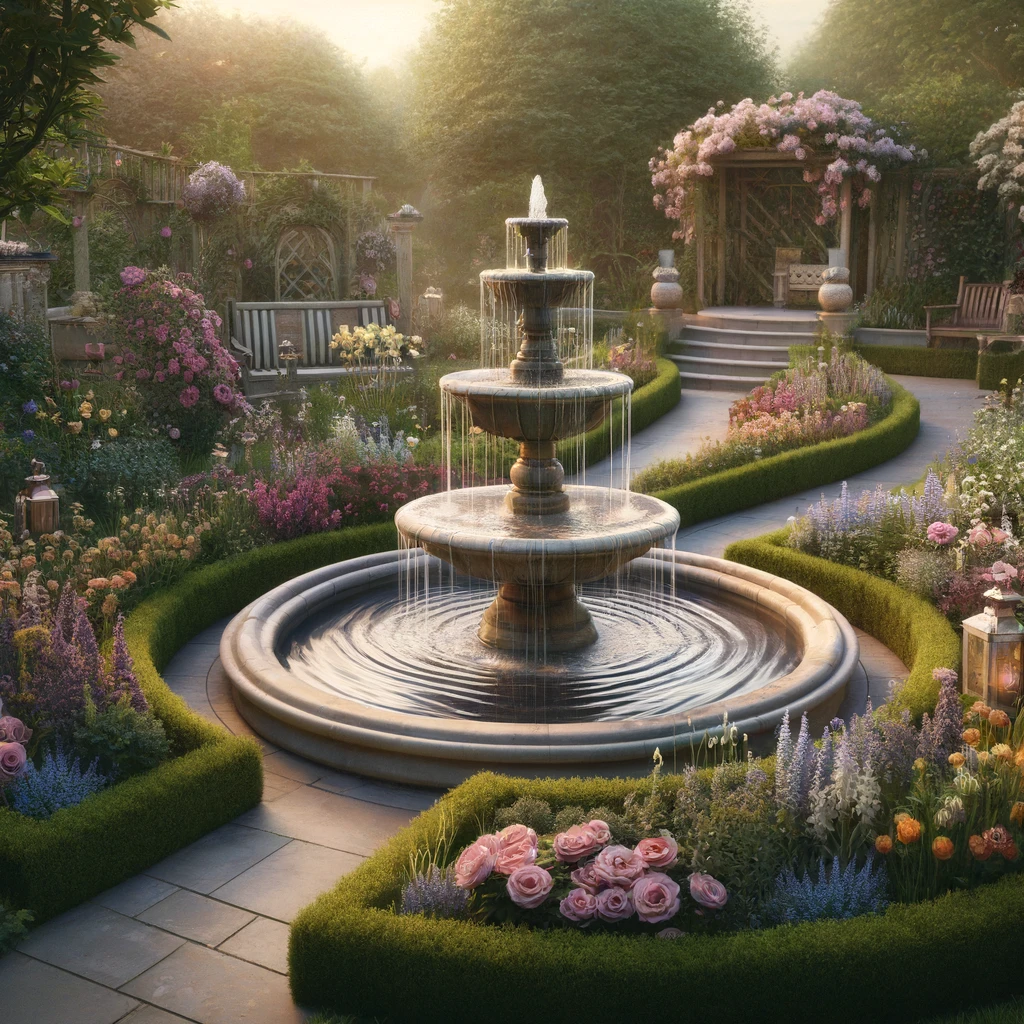

Stable Diffusion allows deeper layout precision, while DALL-E keeps things simple with general layout understanding. The choice depends on how much control the user needs.
How Can We Assess the Quality of AI-generated images Across Artistic Styles Like Photorealistic, Anime, and Cyberpunk?
To assess the quality of AI-generated images, we check how well the image matches the style, detail, and prompt. This applies across styles like photorealistic, anime, and cyberpunk.
In photorealistic images, quality is judged by sharp focus, real lighting, natural textures, and lifelike proportions. Common checks include skin texture, reflections, and depth of field.
In anime style, the image should follow 2D shading, big eyes, clean lines, and consistent character design. Quality depends on color balance, expression, and line clarity.
For cyberpunk, good images show neon lighting, dark urban scenes, and tech-heavy environments. Important features include mood, color contrast, and environmental detail.
Tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E all support these styles, but results vary by prompt clarity and model behavior.
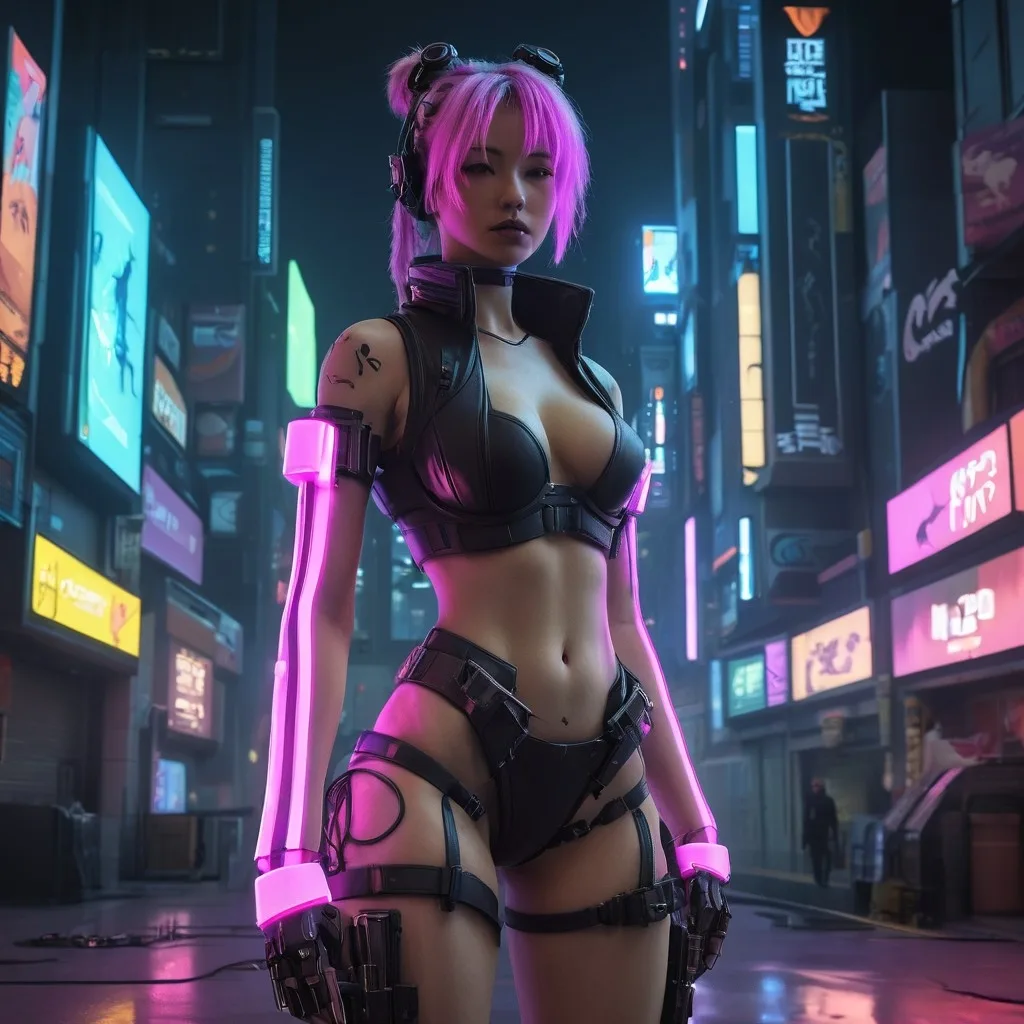
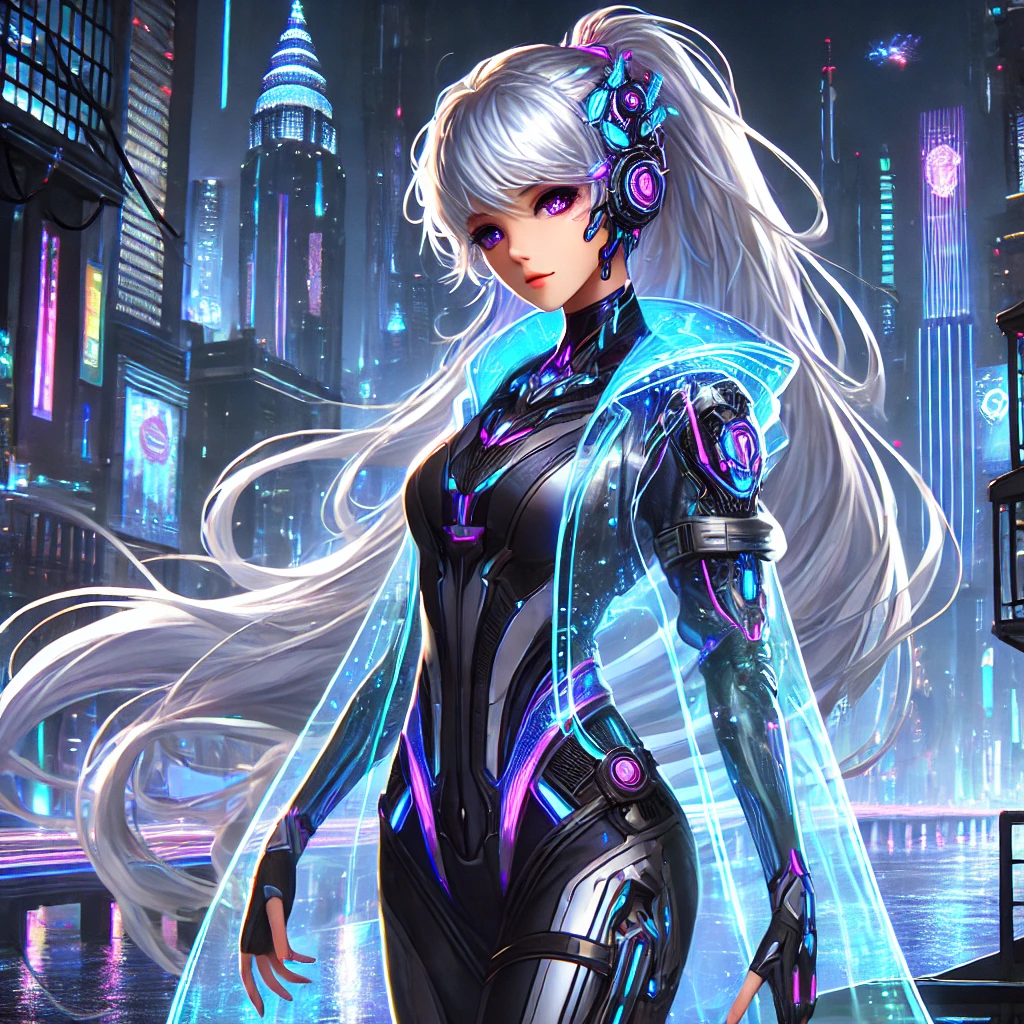



Example prompt:
“female character in cyberpunk city, neon lighting, ultra-detailed, anime style”
Assess quality by checking if the style is consistent, the lighting is vivid, and the details match both cyberpunk and anime elements.
In all cases, image quality depends on matching the visual tone, structure, and emotion expected from the chosen style. Clear prompts and visual balance improve the outcome.
What Is Image-to-Prompt Generation and How Does It Work?
Image-to-prompt generation is the process of creating a text prompt by analyzing an existing image. Instead of writing a prompt first, the AI looks at an image and describes it using words that could recreate the same result. This is also called reverse prompting.
AI models use computer vision, semantic recognition, and image embedding to break down the content of an image. They identify objects, styles, colors, and layouts to generate a meaningful text description. These prompts often include art style, lighting, subject, and mood.
Tools like CLIP Interrogator, PromptPerfect, and DeepAI support image-to-prompt features. Some versions of Stable Diffusion also offer this function for analyzing AI-generated art or photographs.
Example:
An image of a dark city with glowing lights and a robot in the foreground may generate this
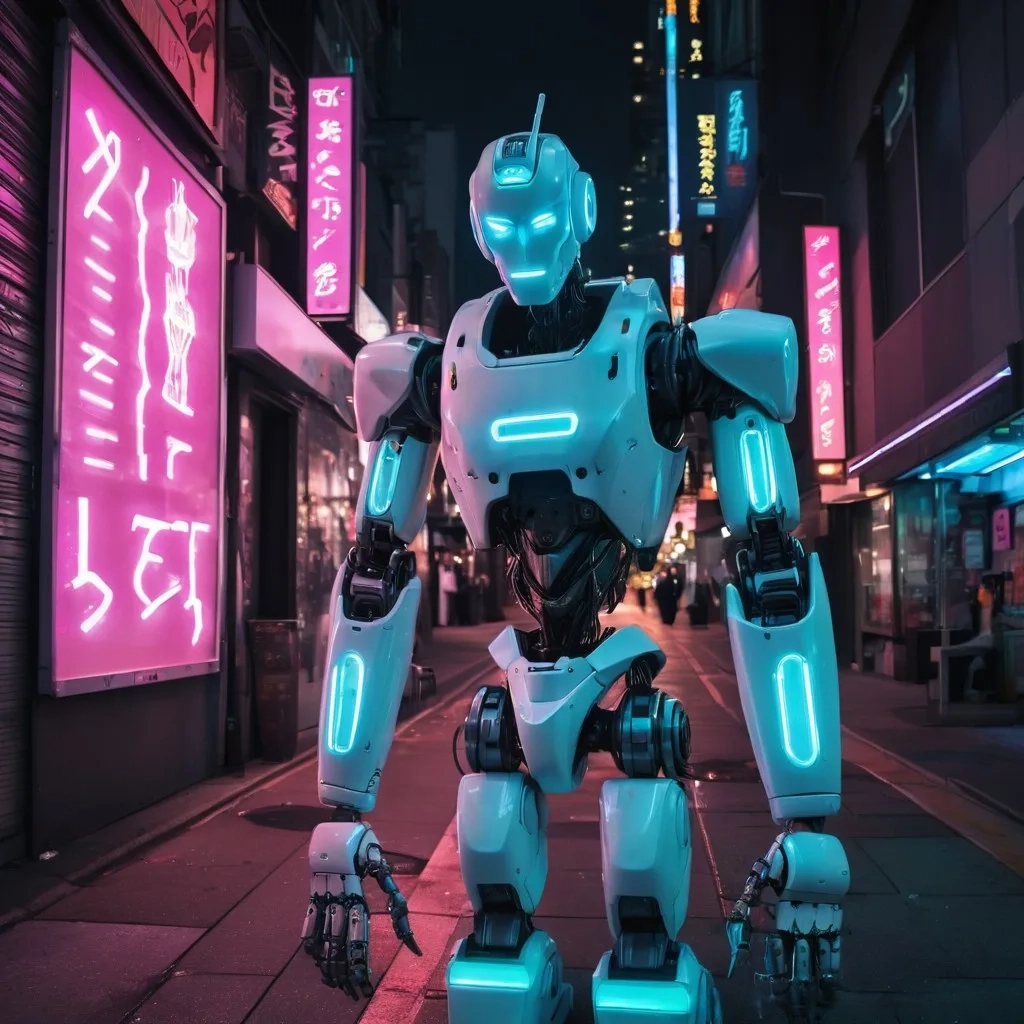
Image to prompt AI to generate a prompt:
“cyberpunk city at night, neon lighting, humanoid robot, sci-fi mood, cinematic tone”
This feature helps creators understand how a prompt affects image style or recreate visuals by copying and editing the generated prompt. It also helps train prompt engineers to write better inputs.
Image-to-prompt tools are useful for reverse-engineering styles, learning prompt language, and improving creative workflows.
What Is the Concept of Image-to-Prompt Technology?
Image-to-prompt technology is a system that takes an image as input and generates a matching text prompt. This process is known as reverse prompting or prompt reconstruction.
The goal is to describe the image clearly so that the same visual can be reproduced using a text-to-image model.
The technology uses AI vision models, feature recognition, and semantic mapping to break the image into meaningful components like objects, style, lighting, and background. It then forms a structured sentence or list that explains what is shown in the image.
For example, an image of a mountain landscape during sunset may generate the following
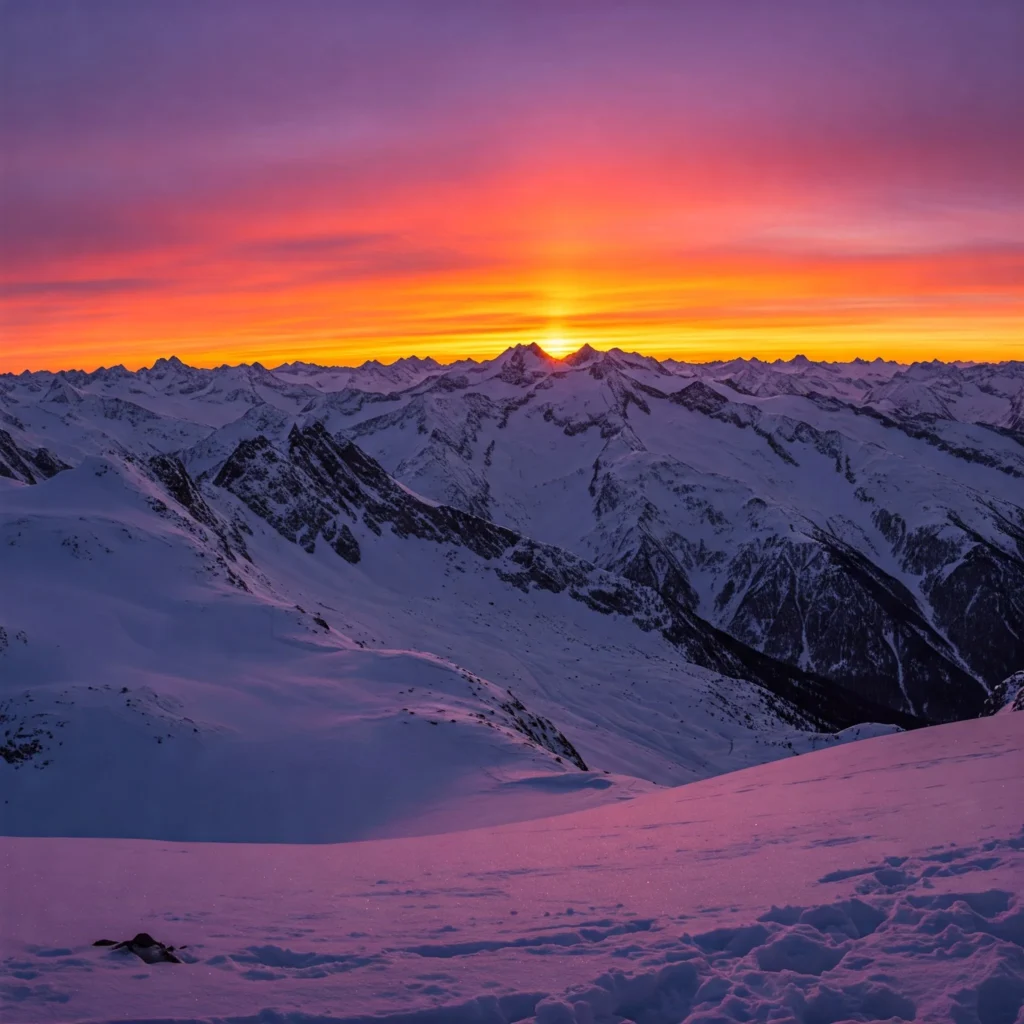

Image to prompt AI to generate a prompt:
“sunset over snowy mountains, warm light, panoramic view, natural colors”
Tools like CLIP Interrogator or image captioning models help extract these details. The result can be used to recreate similar images or learn how specific prompt terms relate to visual styles.
This concept is useful for training, editing, and analyzing AI-generated art. It bridges the gap between image content and prompt language, making prompt creation easier and more accurate.
How Do AI Tools Generate Prompts From Input Images?
AI tools generate prompts from images by using computer vision, image recognition, and natural language processing. These tools study the image, detect its parts, and turn the visual data into descriptive text.
The process starts with object detection, where the AI identifies items like people, animals, buildings, or objects in the image.
Then it analyzes style elements such as lighting, color tone, camera angle, and artistic filters. Finally, the system uses language models to describe everything in a prompt format.
Tools like CLIP Interrogator, DeepAI, and BLIP help generate text from images. They combine visual data with language to build clear and useful prompts.
For example, An image showing a futuristic street at night might generate:
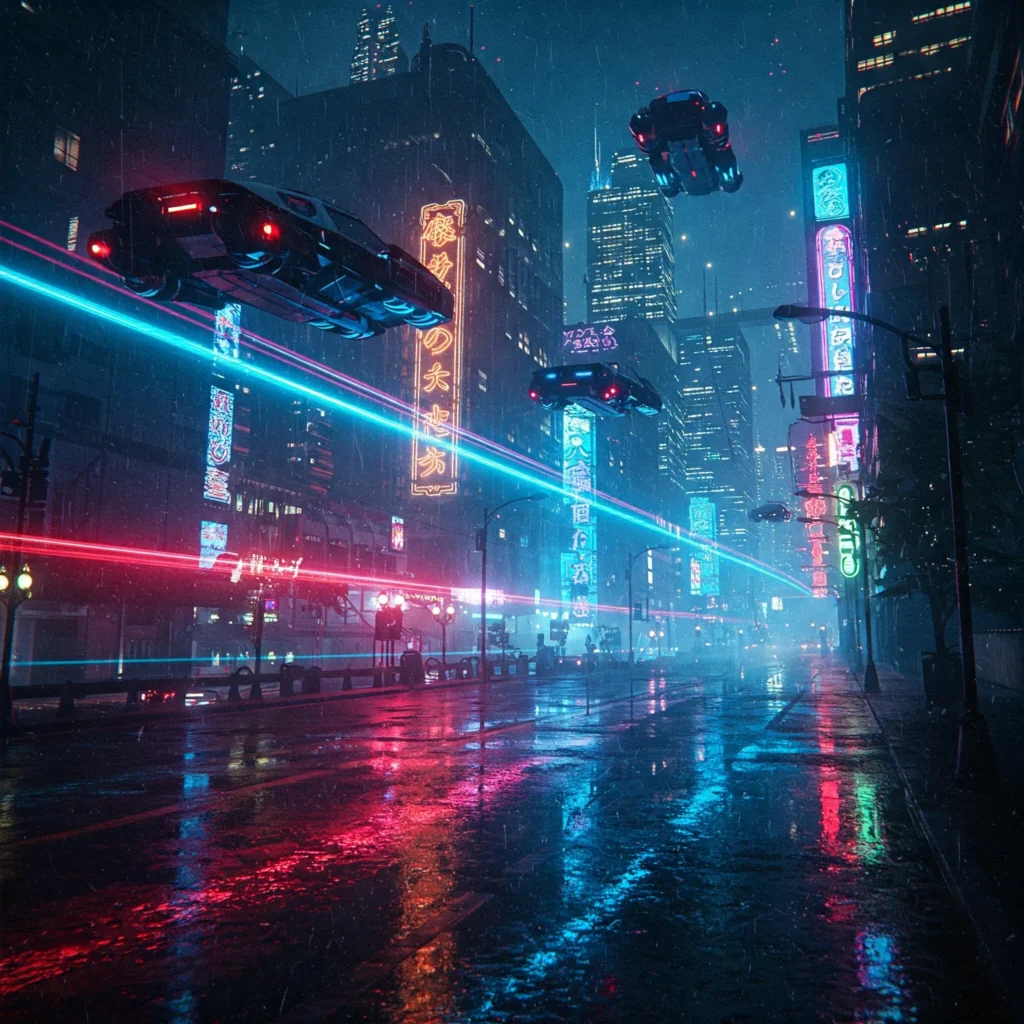

Image to prompt AI to generate a prompt:
“cyberpunk city, neon lights, rainy street, flying cars, cinematic angle”
These generated prompts help users understand image structure, improve prompt writing, or recreate the same style in other tools. The AI links visuals to matching language terms, making the prompt creation automatic and more accurate.
What Are Practical Use Cases of Image-to-Prompt Systems?
Image-to-prompt systems have several practical use cases in creative and technical fields. These tools help users generate clear prompts by analyzing existing images. This saves time, improves results, and supports learning.
One key use is prompt learning. Beginners can upload an image and see what kind of text the AI suggests. This helps them understand how certain words relate to visual features.
Another use is style replication. Artists or designers can use image-to-prompt tools to copy a specific look and apply it to new projects. It works well for anime, photorealism, cyberpunk, and more.
Prompt editing is also common. Users can take a generated prompt and adjust parts of it to get different versions of the same image idea.
In content creation, marketers and designers use this method to turn visual inspiration into prompt-based templates for product visuals, ads, or themes.
For example, A user uploads an image of a cozy coffee shop scene. The system returns:

Image to prompt AI to generate a prompt:
“cozy coffee shop interior, warm lighting, wooden tables, soft focus, autumn vibe”
This prompt can then be reused, edited, or applied in another AI tool.
Image-to-prompt systems are helpful for fast generation, reverse design, and consistent styling across AI-generated visuals.
How to Craft Effective Prompts for AI Models?
Crafting effective prompts helps AI models like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E generate better images. A good prompt tells the AI what you want in terms of subject, style, lighting, and details.
Start with the main subject. Keep it short and specific. Then add style words like “photorealistic,” “anime,” or “oil painting.” Include modifiers such as lighting, camera angle, background, or emotion. You can use commas to separate ideas.
Be clear, avoid long sentences, and focus on strong visual keywords. Each model responds best when prompts match its format: use natural language for DAL-·E, artistic cues for MidJourney, and structured inputs for Stable Diffusion.
Example prompt:
“ancient castle on a mountain, golden hour lighting, cinematic view, high detail, 16:9 aspect ratio”
This tells the model the scene type, time of day, visual tone, and image layout. You can adjust each part for different outputs.
Effective prompts mix subject clarity with visual control. Using the right words in the right order leads to more accurate and high-quality AI-generated images.
What Are the Best Practices for Writing Prompts for MidJourney, DALL-E, and Stable Diffusion?
Writing prompts for AI tools like MidJourney, DALL-E, and Stable Diffusion require a clear structure, visual focus, and the right words to guide the model. Each tool understands prompts differently, so it’s important to match your writing style with how the model processes text.
For MidJourney, the best results come from short, descriptive phrases rather than full sentences. This tool focuses heavily on style, texture, and mood. Use strong visual terms such as “cinematic lighting,” “foggy forest,” or “fantasy artwork.” Separate each detail with commas to make the prompt more readable and effective.
DALL-E works well with natural language. It reads prompts like simple descriptions, so full sentences are okay. This model is good at identifying clear objects and scenes. Keep it descriptive but direct. Focus on what you want the image to show, such as “A mountain range with snowy peaks under a clear sky.”
Stable Diffusion gives more control to the user. You can use prompt modifiers like weights (e.g., (sharp focus:1.2)), negative prompts (e.g., –no blur), and even specific aspect ratios. This allows you to fine-tune the output based on image quality, composition, and unwanted features.
To get high-quality results from any tool, always include the main subject, style, lighting, and resolution or format. Avoid vague terms and be specific about what you want the image to contain or avoid. For example, instead of saying “a city,” write “a futuristic city at night, neon lights, rain, high detail.”
Using the correct prompt format for each model improves the final output. Whether it’s an artistic scene in MidJourney, a literal object in DALL-E, or a customized render in Stable Diffusion, prompt clarity is key to guiding the AI.
What Are the Common Challenges and Fixes in AI Prompting?
AI prompting often brings challenges that affect the quality and accuracy of generated images. Common problems include vague outputs, distorted details, low resolution, or mismatched styles. These issues usually result from unclear prompts, missing visual keywords, or incorrect structure.
One major challenge is overgeneralization. When prompts are too short or abstract, the AI creates broad or unrelated images. For example, writing “fantasy scenes” without context may give random results. To fix this, add details like lighting, color, subject, and mood. A clearer version would be: “fantasy landscape with glowing trees, twilight sky, soft mist, magical atmosphere.”
Another issue is object distortion, such as extra fingers, warped faces, or incorrect anatomy. This often happens when the prompt lacks clarity or has too many concepts. The solution is to simplify the prompt and use negative prompts in models like Stable Diffusion to remove errors, for example: “portrait, detailed face, soft lighting, -no blur,-no extra limbs.”
Style mismatch is also common. If you want a specific art style but don’t name it, the model may use its default setting. Adding terms like “anime style,” “oil painting,” or “digital art” guides the output more accurately.
Low image quality is another challenge, especially with resolution or aspect ratio. In MidJourney or Stable Diffusion, using modifiers like “–ar 16:9” or “8k, ultra-detailed” helps fix sharpness and framing.
Writing prompts for AI models requires both precision and structure. By fixing weak areas like unclear subjects, missing style tags, or forgotten prompt modifiers, you can get better, more consistent results.
What Are the Most Common Mistakes to Avoid When Crafting AI Prompts?
Crafting prompts for AI image generation requires clarity and focus. Many users make common mistakes that reduce image quality or cause unexpected results.
One of the biggest mistakes is using vague or generic language. Prompts like “a cool scene” or “a nice portrait” don’t give the AI enough information to produce accurate images. Always use clear nouns, adjectives, and style terms like “a portrait of an old man, oil painting, soft lighting, warm tones.”
Another mistake is overloading the prompt with too many unrelated elements. Trying to combine too many subjects, styles, or effects can confuse the model. Instead, focus on one main idea with a few supporting details.
Some prompts miss style or resolution tags, which leads to default or low-detail images. Always include keywords like “photorealistic,” “8k,” or “digital art” if high quality or a specific style is needed.
Users sometimes ignore negative prompting in tools like Stable Diffusion. Without it, unwanted elements may appear. For example, if hands often appear distorted, add “–no extra fingers” to improve accuracy.
Poor word order is another issue. Important visual terms should come early in the prompt, as models often prioritize the start of the sentence.
Avoiding these mistakes leads to better control, style accuracy, and image clarity. A simple, well-structured prompt always performs better than a long or unclear one.
How Do Prompt Length and Keyword Placement Affect AI-generated Images?
The length of a prompt and where you place keywords directly affect how AI models generate images.
Prompts that are too short often lack the detail needed for accurate results. On the other hand, very long prompts can confuse the model, especially if the key elements are placed too late in the sentence.
Most AI models prioritize the first few keywords in a prompt. These early terms guide the main subject and overall structure of the image.
That’s why important details like subject, style, or lighting should appear at the beginning. Supporting terms like background elements or camera angles can come later.
Prompt length should stay focused. Keep it long enough to describe the main idea clearly, but short enough to avoid dilution. Clear separation using commas or structured formatting helps the model understand each part better.
A comparison of a short, vague prompt vs. a slightly longer but clearer prompt.

Example of effective keyword placement:
“ancient temple, sunset lighting, cinematic view, jungle background, wide-angle lens”
Here, the subject (“ancient temple”) is first, followed by key visual attributes in order of importance.

Good keyword placement improves image accuracy, style consistency, and output quality. Keeping prompts clear, structured, and well-balanced helps all major AI models perform better.
What Causes Distorted or Blurry AI-Generated Images and How Can They Be Fixed?
Distorted or blurry AI-generated images are common issues caused by weak prompts, missing quality settings, or unclear instructions.
One main reason is the lack of focus keywords like “sharp,” “detailed,” or “high resolution.” When these terms are missing, AI models may produce soft, unfocused visuals.
Another cause is a confusing prompt structure. Overloading a prompt with mixed elements can lead to blending errors, especially in facial features, hands, or background objects. Tools like Stable Diffusion allow fixes using negative prompts such as “–no blur” or “–no distorted face” to avoid specific problems.
Low-resolution settings or automatic compression in tools like DALL-E can also reduce image clarity. To improve this, use terms like “4k,” “8k,” or “ultra-detailed” in the prompt. In MidJourney, adding “-quality 2” or upscaling options often helps produce sharper results.
Example fix prompt:
“portrait of a woman, sharp focus, ultra-detailed, soft background, –no blur, –no double eyes”
To avoid distortion, keep prompts focused, use quality-related terms, and apply prompt modifiers. These adjustments help the AI create clear, balanced, and accurate images.
How Do Prompt Variations Influence Lighting, Depth of Field, and Resolution in AI Images?
Prompt variations can change how AI models render lighting, depth of field, and image resolution. Small changes in wording or order affect how the model interprets visual effects.
For lighting, using specific terms like “soft light,” “harsh shadows,” or “golden hour” guides the mood and brightness. For example, “cinematic lighting” adds contrast and focus, while “ambient lighting” creates a soft, even glow.
To control depth of field, include camera terms like “bokeh,” “shallow focus,” or “background blur.” These help AI simulate photography effects, making the subject stand out.
Resolution is influenced by modifiers such as “4k,” “8k,” “ultra-detailed,” or “high-definition.” Without these, images may look simple or flat, especially in tools like MidJourney or Stable Diffusion.
Example:
“portrait, soft golden lighting, shallow depth of field, ultra-detailed, 8k resolution”
This prompt creates a focused, high-resolution image with a cinematic style.
Changing the prompt structure by reordering keywords or adding/removing modifiers affects the output. Specific words help the AI model apply realistic effects and improve visual quality.
What Are the Most Frequent AI Image Rendering Errors and Their Solutions?
AI-generated images often face rendering errors that affect quality and realism. The most common issues include distorted anatomy, blurred details, extra limbs, unrealistic lighting, and object duplication. These problems usually result from unclear prompts, missing modifiers, or overcomplicated inputs.
For face or hand distortion, simplify the prompt and use negative phrases like “–no extra fingers” or “–no warped face.” Tools like Stable Diffusion allow specific correction through prompt weighting and control tags.
Blurred outputs are usually caused by missing resolution keywords. Add “sharp focus,” “8k,” or “ultra-detailed” to improve clarity.
When objects repeat unnaturally, it’s often due to vague or overly generic descriptions. Be specific about quantity and structure, use terms like “single subject” or “centered view.”
Lighting issues, such as harsh contrast or flat scenes, can be fixed with modifiers like “soft shadows,” “natural light,” or “cinematic lighting.”
Example fix prompt:
“portrait of a man, sharp focus, soft lighting, –no blur, –no extra limbs, centered composition”
Correcting these errors with focused prompts and visual modifiers helps AI models produce clear, balanced, and more accurate images.
What Are the Optimal Prompt Settings for Producing Ultra-Detailed AI-Generated Images?
To produce ultra-detailed AI-generated images, prompts must include specific settings that guide the model toward high resolution, sharp focus, and fine textures. Using strong visual descriptors and quality-related terms is key to achieving clarity.
Start with the main subject, then add detail modifiers such as “ultra-detailed,” “high definition,” “8k resolution,” or “sharp texture.” These signal the model to focus on precision. Include lighting cues like “soft shadows,” “realistic highlights,” or “cinematic lighting” to enhance depth.
In tools like Stable Diffusion, you can also use weighting, for example, “(sharp focus:1.3)” to increase detail on key elements. MidJourney allows enhanced quality using flags like “ quality 2” or prompt terms like “hyper-realistic.”
Example of a strong, detailed prompt:
“ancient temple in jungle, ultra-detailed, sharp focus, soft light, 8k, moss textures, cinematic atmosphere”
The combination of resolution terms, material cues, and lighting produces sharp, rich images. Keeping the prompt balanced, with no conflicting details, helps the AI render complex textures clearly.
Precise, layered prompts improve image sharpness, texture clarity, and depth, especially in styles like photorealism or concept art.
How Do Weighting Adjustments Affect Image Results in MidJourney Compared to Stable Diffusion?
Weighting adjustments help control how strongly certain parts of a prompt influence the final image. This feature works differently in MidJourney and Stable Diffusion, affecting how the models balance style, subject, and detail.
In Stable Diffusion, users can apply exact weights using parentheses and numeric values. For example, “(sharp focus:1.5)” increases emphasis on that part, while “(background blur:0.5)” reduces it. This allows fine control over each visual element, making the output more precise.
MidJourney doesn’t support numeric weighting the same way, but it uses natural keyword priority. Words at the beginning of the prompt or repeated terms hold more influence. Users can adjust results using prompt length, repetition, or MidJourney’s stylize and quality settings to guide balance and detail.
Example for Stable Diffusion:
“portrait of a man, (sharp eyes:1.4), (blurred background:0.6), cinematic light, ultra-detailed”

model: stable diffusion
Example for MidJourney (natural weighting):
“man portrait, sharp eyes, cinematic light, ultra-detailed, soft background”

model: midjourney
While Stable Diffusion allows technical weighting, MidJourney focuses on stylistic balance. Both systems respond well to clear, focused prompts, but Stable Diffusion offers more direct control for advanced users.
How Can You Apply Effective Color Grading and Lighting Adjustments in AI Prompts?
To apply color grading and lighting adjustments in AI image prompts, you must use clear visual terms that guide the model’s tone and atmosphere. These elements help define the mood, time of day, and style of the image.
For lighting, include terms like “soft light,” “backlit,” “harsh shadows,” or “golden hour” to shape the visual depth and direction. Words like “cinematic lighting” or “ambient glow” add emotional tone and contrast to the scene.
Color grading focuses on color balance and style. Use phrases such as “warm tones,” “cool blue filter,” “high contrast,” “vintage film color,” or “teal and orange grading” to apply a specific mood or effect. These prompts help simulate photography or film-style visuals.
Both MidJourney and Stable Diffusion respond well to these adjustments when they are placed early or clearly within the prompt. They can also be combined with resolution and detail modifiers for a sharper result.
Example prompt:
“urban rooftop at sunset, soft warm light, cinematic shadows, teal and orange color grading, high detail”
This prompt creates a dramatic, visually styled scene with warm lighting and a strong color theme.
Using the right lighting and color terms in your prompt allows the AI to produce consistent, stylized, and emotionally rich images.
How Can You Generate Hyper-Realistic Images with Cinematic Lighting Using AI Prompts?
To generate hyper-realistic images with cinematic lighting, your AI prompt must include detailed terms for texture, lighting effects, and visual depth. Hyper-realism requires focus on fine details, while cinematic lighting adds emotion through contrast, shadows, and directional light.
Use keywords like “photo-realistic,” “sharp focus,” “ultra-detailed,” and “high resolution” to guide the model toward lifelike results. For cinematic lighting, include phrases such as “soft shadows,” “rim lighting,” “dramatic backlight,” or “golden hour glow.” These lighting terms help define the scene’s mood and realism.
MidJourney and Stable Diffusion both support this style well when prompts are structured with strong visual cues. You can also add camera-related terms like “85mm lens,” “depth of field,” or “bokeh effect” to increase realism.
Example prompt:
“portrait of a man, photo-realistic, cinematic lighting, soft shadows, ultra-detailed skin, shallow depth of field, 85mm lens”
This prompt tells the AI to focus on lighting mood, sharp facial detail, and realistic composition.
Combining lighting style with hyper-realistic modifiers in your prompt helps the AI create vivid, lifelike images with depth, emotion, and professional visual quality.
What Are the Best AI Prompt Modifiers for Creating Anime-Style Image Generation?
To create high-quality anime-style images with AI, using the right prompt modifiers is essential. These modifiers help define the look, style, and details that match Japanese animation aesthetics. Popular models like Stable Diffusion (Waifu Diffusion) and MidJourney respond well to anime-specific keywords.
Start with visual style terms like “anime style,” “manga drawing,” “2D illustration,” or “cel shading.” These tell the model to use flat colors, bold lines, and large, expressive eyes. Add modifiers for face and hair, such as “sparkling eyes,” “detailed hair strands,” or “smooth skin.”
To guide the mood or setting, include phrases like “pastel background,” “school uniform,” “sakura trees,” or “fantasy anime scene.” Lighting effects such as “soft glow,” “dramatic sunset,” or “light bloom” help enhance the anime look.
Example prompt:
“anime girl, pink hair, school uniform, big sparkling eyes, cel-shaded, pastel background, soft light”
This prompt gives a clear structure and style for the AI to follow, resulting in a clean, stylized anime image.
Using focused modifiers improves consistency in line art, color balance, and overall theme. This helps the AI deliver images that match well-known anime design standards.
What Is the Future of AI Image Prompting?
The future of AI image prompting is moving toward more intelligent, personalized, and automated systems. Prompting will no longer rely only on text. Instead, AI models will use multimodal inputs, a mix of text, images, voice, and gestures to understand creative intent more deeply.
One major change will be the rise of prompt recommendation engines that suggest prompt structures, modifiers, and style presets based on user goals. This will make image generation faster and more accessible, especially for beginners.
As models like Stable Diffusion, MidJourney, and DALL-E evolve, they will improve in context recognition, adjusting to the tone, mood, and visual theme without detailed instructions. Tools will also support interactive editing, where users can modify images live without re-prompting from scratch.
Advanced features like style memory, real-time rendering, and emotion-aware visuals are expected. These will let creators maintain consistent art styles across projects.
Example: In the future, a user might say,
“Create a peaceful lake scene in Studio Ghibli style”
The AI will instantly generate the image, adjust colors, and animate water movement all without writing a detailed prompt.0
AI image prompting is becoming more intuitive, helping users focus on creativity while the model handles technical control.
What Are the Emerging Trends in Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is evolving rapidly as generative AI tools become more advanced. One major trend is the shift toward modular prompt templates, where users combine reusable parts like subject, style, and modifiers to build complex prompts faster. These templates improve consistency and reduce manual errors.
Another trend is automated prompt optimization, where AI systems suggest better words, structure, or weights to improve image results. These tools help users, especially beginners, craft better prompts using fewer trial-and-error attempts.
Multimodal prompt systems are also emerging. These systems use a mix of text, images, and audio to guide generation more naturally. AI can now recognize intent across different inputs and respond with more precise outputs.
Style tagging is becoming common, too. Users can save preferred looks or formats, like “cyberpunk city” or “soft anime portrait,” and reuse them with new subjects for faster creation.
Example: A prompt editor might recommend this based on user history
“ancient warrior, dramatic lighting, ultra-detailed, oil painting style”
by learning from previous prompts and suggesting optimized terms.
These trends make prompt engineering faster, more accurate, and more personalized, giving creators better control over AI-generated visuals.
Can AI Prompts Replace Traditional Graphic Designers?
AI prompts can create high-quality visuals quickly, but they cannot fully replace traditional graphic designers. While tools like MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E can generate images from text, they still need human input for concept clarity, brand alignment, and final edits.
AI excels at producing fast results for concept art, social media posts, or quick mockups. However, it struggles with creative direction, brand consistency, and design systems that professionals manage in real projects.
Designers bring value through layout control, typography, color theory, and custom revisions tasks that AI cannot fully understand or apply without guidance. Human creativity and strategy remain essential for complex design needs.
Example: A prompt like
“tech company logo, blue tones, minimal style”
It may give a good draft, but it still needs a designer to adjust proportions, align branding, and prepare it for print or web formats.
In short, AI prompts are a powerful tool for supporting design, but they work best when guided by human creativity, not as a full replacement.